Development of real-time and lateral flow dipstick recombinase polymerase amplification assays for rapid detection of goatpox virus and sheeppox virus
- PMID: 28716095
- PMCID: PMC5514530
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-017-0792-7
Development of real-time and lateral flow dipstick recombinase polymerase amplification assays for rapid detection of goatpox virus and sheeppox virus
Abstract
Background: Goatpox virus (GTPV) and sheeppox virus (SPPV), which belong to the Capripoxvirus (CaPV), are economically important pathogens of small ruminants. Therefore, a sensitive, specific and rapid diagnostic assay for detection of GTPV and SPPV is necessary to accurately and promptly control these diseases.
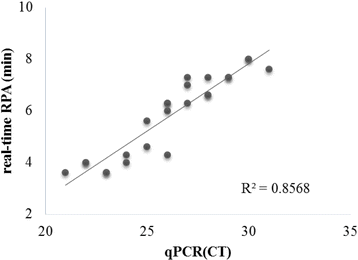
Methods: Recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) assays combined with a real-time fluorescent detection (real-time RPA assay) and lateral flow dipstick (RPA LFD assay) were developed targeting the CaPV G-protein-coupled chemokine receptor (GPCR) gene, respectively.
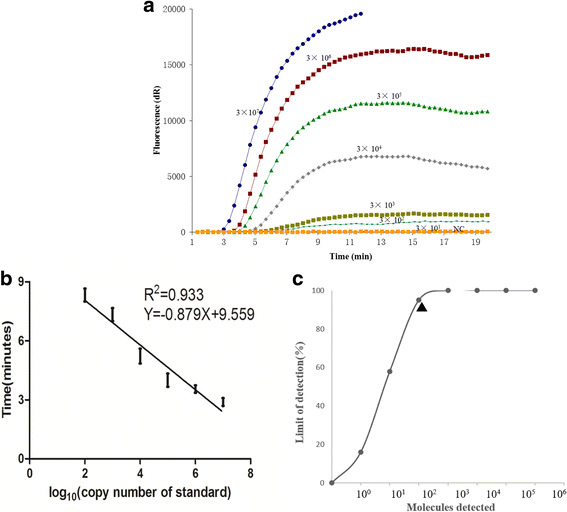
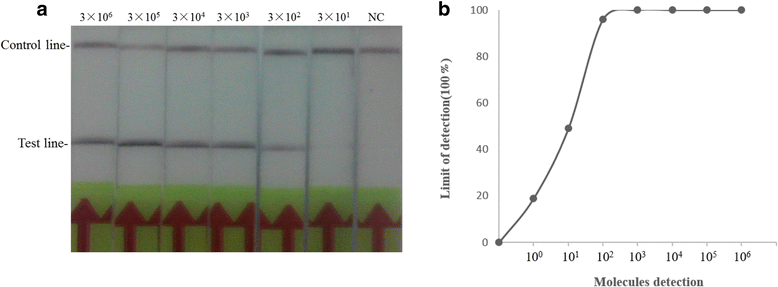
Results: The sensitivity of both CaPV real-time RPA assay and CaPV RPA LFD assay were 3 × 102 copies per reaction within 20 min at 38 °C. Both assays were highly specific for CaPV, with no cross-reactions with peste des petits ruminants virus, foot-and-mouth disease virus and Orf virus. The evaluation of the performance of these two assays with clinical sample (n = 107) showed that the CaPV real-time RPA assay and CaPV RPA LFD assay were able to specially detect SPPV or GTPV present in samples of ovine in liver, lung, kidney, spleen, skin and blood.
Conclusions: This study provided a highly time-efficient and simple alternative for rapid detection of GTPV and SPPV.
Keywords: CaPV RPA LFD; CaPV real-time RPA; Goatpox virus; Recombinase polymerase amplification; Sheeppox virus.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This work was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (approval number LVRIAEC 2012–018). Tissue samples were collected from sheep and goat based on good animal practices of the Animal Ethics Procedures and Guidelines of the People’s Republic of China (AEPGPRC). Tissue samples were collected from the livestock with owner consent as routine disease surveillance. All study participants provided written and informed consent.
Consent for publication
Written informed consents for publication have been obtained from all the participants.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Multiplex PCR for simultaneous detection and differentiation of sheeppox, goatpox and orf viruses from clinical samples of sheep and goats.J Virol Methods. 2014 Jan;195:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2013.10.009. Epub 2013 Oct 14. J Virol Methods. 2014. PMID: 24134940
-
TaqMan based real-time duplex PCR for simultaneous detection and quantitation of capripox and orf virus genomes in clinical samples.J Virol Methods. 2014 Jun;201:44-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2014.02.007. Epub 2014 Feb 16. J Virol Methods. 2014. PMID: 24552953
-
Development of the isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification assays for rapid detection of the genus Capripoxvirus.J Virol Methods. 2023 Oct;320:114788. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2023.114788. Epub 2023 Jul 28. J Virol Methods. 2023. PMID: 37517457
-
Construction of recombinant capripoxviruses as vaccine vectors for delivering foreign antigens: Methodology and application.Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019 Aug;65:181-188. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2019.05.013. Epub 2019 May 18. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31300111 Review.
-
Overview of diagnostic tools for Capripox virus infections.Prev Vet Med. 2020 Aug;181:104704. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2019.104704. Epub 2019 May 28. Prev Vet Med. 2020. PMID: 31196699 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid and sensitive detection of pathogenic Elizabethkingia miricola in black spotted frog by RPA-LFD and fluorescent probe-based RPA.Fish Shellfish Immunol Rep. 2022 Jun 24;3:100059. doi: 10.1016/j.fsirep.2022.100059. eCollection 2022 Dec. Fish Shellfish Immunol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36419595 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of Francisella noatunensis subsp. orientalis.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 14;13(2):e0192979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192979. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29444148 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitive and semiquantitative detection of soil-transmitted helminth infection in stool using a recombinase polymerase amplification-based assay.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Sep 13;15(9):e0009782. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009782. eCollection 2021 Sep. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34516554 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and simple detection of Phytophthora cactorum in strawberry using a coupled recombinase polymerase amplification-lateral flow strip assay.Phytopathol Res. 2021;3(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s42483-021-00089-8. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Phytopathol Res. 2021. PMID: 34127941 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinase polymerase amplification assay combined with a dipstick-readout for rapid detection of Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae infections.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 4;16(2):e0246573. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246573. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33539437 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

