Post-stroke depression in Ghana: Characteristics and correlates
- PMID: 28716256
- PMCID: PMC5542581
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jns.2017.06.032
Post-stroke depression in Ghana: Characteristics and correlates
Abstract
Background: Poststroke depression (PSD) is prevalent and is an important determinant of functional recovery, quality of life and mortality after stroke. Scanty data on the nature of PSD among stroke survivors in sub-Saharan Africa prompted this study.
Objective: To assess the prevalence and predictors of depression in a convenience sample of Ghanaian stroke survivors.
Methods: We evaluated consecutive stroke survivors encountered at a comprehensive neurology clinic in a tertiary medical center in Ghana. The Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) and Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS) were both used to screen for depressive symptoms and subjects were considered as depressed if they scored ≥16 on the CES-D scale and >5 on the GDS. Demographic and clinical data on stroke type and severity as well as health-related quality of life indicators were collected. Predictors of stroke-related depression were assessed using a logistic regression model.
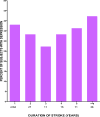
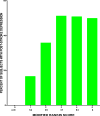
Results: Of 200 stroke survivors, mean±SD age was 62.0±14.4years, and 105 (52.5%) patients were men. Among the cohort 78.5% were classified as being depressed by CES-D, 42.5% by GDS, and 36.5% on both CES-D and GDS. In multivariable analyses, for each unit increase on the Modified Rankin scale (i.e. worsening disability), there were higher odds of depression (adjusted OR 1.85; 1.28-2.69, p=0.001), and being divorced (vs. being married) was linked to depression (adjusted 2.82; 1.18-6.71, p=0.02). Stroke survivors with depression demonstrated profound diminutions in the physical, psycho-social, cognitive and eco-social domains of quality of life compared with those without depression (p<0.05).
Conclusion: Almost 4 out of 10 stroke survivors in this Ghanaian cohort displayed clinically significant depression. Prospective interventional studies are urgently needed to provide solid evidence-based and culturally tailored interventions to address post-stroke depression particularly in LMICs.
Keywords: Disability; Ghana; Post-stroke depression; Quality of life.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Post-stroke depression: Risk assessment.J Neurol Sci. 2018 Apr 15;387:228. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2018.01.034. Epub 2018 Jan 31. J Neurol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29395093 No abstract available.
-
Response by Sarfo and Ovbiagele to letter regarding "Post-stroke depression: Risk assessment".J Neurol Sci. 2018 Apr 15;387:229-230. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2018.01.033. Epub 2018 Jan 31. J Neurol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29395682 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hackett ML, Pickles K. Part I: frequency of depression after stroke: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Int J Stroke. 2014;9:1017–1025. - PubMed
-
- Kutlubaev MA, Hackett ML. Part II: predictors of depression after stroke and impact of depression on stroke outcome: an updated systematic review of observational studies. Int J Stroke. 2014;9:1026–1036. - PubMed
-
- Ayerbe L, Ayis S, Crichton S, Wolfe CD, Rudd AG. The natural history of depression up to 15 years after stroke: the South London Stroke Register. Stroke. 2013;44:1105–1110. - PubMed
-
- Hackett ML, Yapa C, Parag V, Anderson CS. Frequency of depression after stroke: a systematic review of observational studies. Stroke. 2005;36:1330–1340. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical