Negative Regulation of Cytokine Signaling in Immunity
- PMID: 28716890
- PMCID: PMC6028070
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028571
Negative Regulation of Cytokine Signaling in Immunity
Abstract
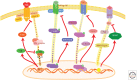
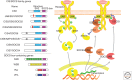
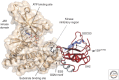
Cytokines are key modulators of immunity. Most cytokines use the Janus kinase and signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK-STAT) pathway to promote gene transcriptional regulation, but their signals must be attenuated by multiple mechanisms. These include the suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) family of proteins, which represent a main negative regulation mechanism for the JAK-STAT pathway. Cytokine-inducible Src homology 2 (SH2)-containing protein (CIS), SOCS1, and SOCS3 proteins regulate cytokine signals that control the polarization of CD4+ T cells and the maturation of CD8+ T cells. SOCS proteins also regulate innate immune cells and are involved in tumorigenesis. This review summarizes recent progress on CIS, SOCS1, and SOCS3 in T cells and tumor immunity.
Copyright © 2018 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aman MJ, Migone TS, Sasaki A, Ascherman DP, Zhu M, Soldaini E, Imada K, Miyajima A, Yoshimura A, Leonard WJ. 1999. CIS associates with the interleukin-2 receptor β chain and inhibits interleukin-2-dependent signaling. J Biol Chem 274: 30266–30272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
