Clinical Features, Pathogenesis, and Treatment of Large Granular Lymphocyte Leukemias
- PMID: 28717070
- PMCID: PMC5548667
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.56.8881
Clinical Features, Pathogenesis, and Treatment of Large Granular Lymphocyte Leukemias
Abstract
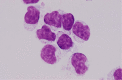
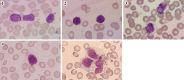
Large granular lymphocytes (LGLs) are large lymphocytes with azurophilic granules in their cytoplasm. LGLs are either natural killer (NK) cells or T lymphocytes. Expansions of the LGLs in the peripheral blood are seen in various conditions, including three clonal disorders: T-cell LGL (T-LGL) leukemia, chronic lymphoproliferative disorders of NK cells (CLPD-NK), and aggressive NK-cell leukemia (ANKL). However, the monoclonal and polyclonal expansion of LGLs has been associated with many other conditions. The present article describes these LGL disorders, with special emphasis on the clinical features, pathogenesis, and treatments of the three above-mentioned clonal disorders.
Keywords: LGL; T-LGL leukemia; aggressive NK-cell leukemia; chronic lymphoproliferative disorders of NK cells.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al. , Eds. IARC Press, Lyon, 2008: 272-277.
-
- Buchanan JD, Fairley KF, Barrie JU. Return of spermatogenesis after stopping cyclophosphamide therapy. Lancet 2: 156-157, 1975. - PubMed
-
- Loughran TP, Marshall EK, Starkebaum G, et al. . Leukemia of large granular lymphocytes: association with clonal chromosomal abnormalities and autoimmune neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and hemolytic anemia. Ann Intern Med 102: 169-175, 1985. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

