Blood Pressure and Penumbral Sustenance in Stroke from Large Vessel Occlusion
- PMID: 28717354
- PMCID: PMC5494536
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00317
Blood Pressure and Penumbral Sustenance in Stroke from Large Vessel Occlusion
Abstract
The global burden of stroke remains high, and of the various subtypes of stroke, large vessel occlusions (LVOs) account for the largest proportion of stroke-related death and disability. Several randomized controlled trials in 2015 changed the landscape of stroke care worldwide, with endovascular thrombectomy (ET) now the standard of care for all eligible patients. With the proven success of this therapy, there is a renewed focus on penumbral sustenance. In this review, we describe the ischemic penumbra, collateral circulation, autoregulation, and imaging assessment of the penumbra. Blood pressure goals in acute stroke remain controversial, and we review the current data and suggest an approach for induced hypertension in the acute treatment of patients with LVOs. Finally, in addition to reperfusion and enhanced perfusion, efforts focused on developing therapeutic targets that afford neuroprotection and augment neural repair will gain increasing importance. ET has revolutionized stroke care, and future emphasis will be placed on promoting penumbral sustenance, which will increase patient eligibility for this highly effective therapy and reduce overall stroke-related death and disability.
Keywords: blood pressure; neuroprotection; penumbra; pressor therapy; stroke; thrombectomy.
Figures
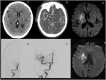
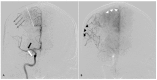
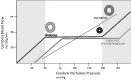

References
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet (2012) 380:2095–128.10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goldstein LB, Adams R, Alberts MJ, Appel LJ, Brass LM, Bushnell CD, et al. Primary prevention of ischemic stroke: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council: cosponsored by the Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease Interdisciplinary Working Group; Cardiovascular Nursing Council; Clinical Cardiology Council; Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism Council; and the Quality of Care and Outcomes Research Interdisciplinary Working Group: the American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline. Stroke (2006) 37:1583–633.10.1161/01.STR.0000223048.70103.F1 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

