CD25 expression and outcomes in older patients with acute myelogenous leukemia treated with plerixafor and decitabine
- PMID: 28718760
- PMCID: PMC5773411
- DOI: 10.1080/10428194.2017.1352089
CD25 expression and outcomes in older patients with acute myelogenous leukemia treated with plerixafor and decitabine
Abstract
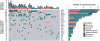
We investigated CD25 expression in older (≥60 years) patients with new acute myelogenous leukemia treated with decitabine and plerixafor. Patients resistant to therapy or survival ≤1 year had significantly higher percentages of CD25pos myeloid blasts in baseline bone marrow. CD25pos patients had an increased odds of resistance compared to CD25neg patients (p = .015). In univariate analysis, we found CD25pos patients had inferior survival compared to CD25neg (p = .002). In patients with intermediate risk cytogenetics, CD25pos status stratified patients associating with inferior survival (p = .002). In multivariable analysis, CD25 and TP53 mutations trended towards predicting remission to therapy but were not predictive of survival. Only remission status, ASXL1 and TET2 mutations were found to independently predict overall survival (OS). We conclude CD25 expression identifies patients at risk for resistance to hypomethylating chemotherapy but does not independently predict OS in an older AML population treated with decitabine and plerixafor.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01352650.
Keywords: AML; CD25; decitabine; drug resistance; prognostication.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
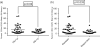

References
-
- Terwijn M, Feller N, van Rhenen A, et al. Interleukin-2 receptor alpha-chain (CD25) expression on leukaemic blasts is predictive for outcome and level of residual disease in AML. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:1692–1699. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
