Association of Interferon- γ Receptor-1 Gene Polymorphism with Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Infection among Iranian Patients with Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 28719321
- PMCID: PMC5508906
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.16-0905
Association of Interferon- γ Receptor-1 Gene Polymorphism with Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Infection among Iranian Patients with Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
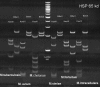
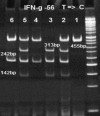
Nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) cause significant pulmonary infections in humans. Researchers have reported an association between interferon-gamma receptor-1 (IFN-γR1 or IFNGR1) deficiency and susceptibility to NTM, but the relevance of polymorphism within these genes is not yet clear. In this study, a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), T to C, at position-56 in NTM patients with pulmonary disease was investigated. Molecular identification of Mycobacterium isolates was performed with hsp65 genes using polymerase chain reaction restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP). Then, the host genomic DNA from confirmed NTM patients (N = 80) and control subjects (N = 80) were screened for SNPs of IFNGR1 (T-56C) by PCR-RFLP. The results indicated that NTM patients had higher TC (26/80; 32.5%) or CC (46/80; 57.5%) genotypes in comparison with control groups (TC genotypes [22/80, 27.5%]; CC genotypes [6/80, 7.5%]) (P < 0.05). In this regard, all the patients infected with rapid-growing Mycobacterium (RGM, i.e., Mycobacterium chelonae and Mycobacterium fortuitum) had CC genotypes (100%). In contrary, only 50.7% (35/69) of infected patients with slow-growing Mycobacterium (i.e., Mycobacterium simiae, Mycobacterium kansasii, and Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare) had CC genotypes. Thus, patients with CC mutation in IFNGR1 at position-56 are more likely to develop RGM infection. In overall, there is a significant association between SNP of IFNGR1 at position-56 and susceptibility to NTM infection. Based on these data, we propose SNP of IFNGR1 at position-56 as a suitable "biomarker" for identifying populations at higher risk of infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The importance of single nucleotide polymorphisms in interferon gamma receptor-1 gene in pulmonary patients infected with rapid grower mycobacterium.Int J Mycobacteriol. 2016 Dec;5 Suppl 1:S210-S211. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmyco.2016.09.040. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Int J Mycobacteriol. 2016. PMID: 28043560
-
Polymorphisms of interferon-gamma and interferon-gamma receptor 1 genes and non-tuberculous mycobacterial lung diseases.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2007 Mar;87(2):166-71. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2006.07.003. Epub 2006 Oct 4. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2007. PMID: 17023216
-
IFNGR1, IRF8 genetic polymorphisms modulate the susceptibility of non-tuberculous mycobacteria pulmonary disease and influence the patients' treatment outcomes and immune status.Inflamm Res. 2025 Jul 22;74(1):106. doi: 10.1007/s00011-025-02071-y. Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40691380
-
[Susceptibility genes for nontuberculous mycobacterial disease].Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2017;40(1):60-67. doi: 10.2177/jsci.40.60. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2017. PMID: 28539556 Review. Japanese.
-
An overview of pulmonary infections due to rapidly growing mycobacteria in South Asia and impressions from a subtropical region.Int J Mycobacteriol. 2020 Jan-Mar;9(1):62-70. doi: 10.4103/ijmy.ijmy_179_19. Int J Mycobacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32474491 Review.
Cited by
-
Apoptotic effects of cold atmospheric pressure plasma on A549 and LL/2 lung carcinoma cell lines.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 4;15(1):19567. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-03934-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40467678 Free PMC article.
-
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in IFN-γ Signaling Pathway Associated with Risk of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Chinese Children.Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2020 Jan 22;2020:8121659. doi: 10.1155/2020/8121659. eCollection 2020. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32047575 Free PMC article.
-
Supporting Patients with Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Disease: Ensuring Best Practice in UK Healthcare Settings.Pharmacy (Basel). 2024 Aug 21;12(4):126. doi: 10.3390/pharmacy12040126. Pharmacy (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39195855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Distribution Frequency of Interferon-Gamma Receptor 1 Gene Polymorphisms in Interferon-γ Release Assay-Positive Patients.Dis Markers. 2017;2017:4031671. doi: 10.1155/2017/4031671. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Dis Markers. 2017. PMID: 29209098 Free PMC article.
-
A gene variation of Interferon Gamma Receptor-I promoter (rs1327474A>G) and chronic hepatitis C virus infection.Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2019 Winter;12(1):46-51. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2019. PMID: 30949319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cassidy PM, Hedberg K, Saulson A, McNelly E, Winthrop KL, 2009. Nontuberculous mycobacterial disease prevalence and risk factors: a changing epidemiology. Clin Infect Dis 49: 124–129. - PubMed
-
- Falkinham JO, 2009. Surrounded by mycobacteria: nontuberculous mycobacteria in the human environment. J Appl Microbiol 107: 356–367. - PubMed
-
- Hruska K, Kaevska M, 2012. Mycobacteria in water, soil, plants and air: a review. Vet Med (Praha) 57: 623–679.
-
- Glassroth J, 2008. Pulmonary disease due to nontuberculous mycobacteria. Chest 133: 243–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

