Case Report: Disseminated Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei and Mycobacterium tuberculosis Coinfection in a Japanese Patient with Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
- PMID: 28719322
- PMCID: PMC5508913
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.16-1004
Case Report: Disseminated Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei and Mycobacterium tuberculosis Coinfection in a Japanese Patient with Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
Abstract
Talaromyces marneffei is a dimorphic fungus endemic mainly in southeast and south Asia. It causes severe mycosis, usually in immunocompromised individuals, such as those with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Concomitant infection with T. marneffei and other opportunistic pathogens is plausible because the majority of T. marneffei infections occur in patients with advanced HIV infection. Nonetheless, coinfection in the same site has rarely been reported, and poses a considerable diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. We report the case of an HIV-infected Japanese patient who had lived in Thailand for 6 years. The patient developed T. marneffei and Mycobacterium tuberculosis coinfection, and both pathogens were isolated from the same sites: a blood specimen and a lymph node aspirate. Clinicians should be aware of concomitant infection with T. marneffei and other pathogens in patients with advanced HIV disease who are living in or who have visited endemic areas.
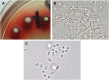
Figures

Similar articles
-
Disseminated Penicillium marneffei infection in southeast Asia.Lancet. 1994 Jul 9;344(8915):110-3. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91287-4. Lancet. 1994. PMID: 7912350
-
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei infection in non-HIV-infected patients.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2016 Mar 9;5(3):e19. doi: 10.1038/emi.2016.18. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2016. PMID: 26956447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disseminated Penicillium marneffei infection in human immunodeficiency virus-infected children.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1995 Nov;14(11):935-40. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199511000-00003. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1995. PMID: 8584358
-
Disseminated Talaromyces marneffei and Mycobacterium intracellulare coinfection in an HIV-infected patient.Int J Infect Dis. 2015 Sep;38:86-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2015.07.020. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Int J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26232630
-
Unusual disseminated Talaromyces marneffei infection mimicking lymphoma in a non-immunosuppressed patient in East China: a case report and review of the literature.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Oct 28;20(1):800. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05526-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33115429 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Coexisting of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma and Talaromyces marneffei Brain Abscess in an AIDS Patient, A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Feb 22;17:709-718. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S432697. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 38410795 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent infection with Talaromyces marneffei and Cryptococcus neoformans in a patient without HIV infection.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Jan;19(1):160-164. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8172. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 31853286 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical features of Talaromyces marneffei infection and colonization in HIV-negative patients: the role of mNGS in diagnosis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 28;12:1579522. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1579522. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40357282 Free PMC article.
-
First case report of Talaromyces marneffei infection in HIV-infected patient in the city of Ouagadougou (Burkina Faso).Med Mycol Case Rep. 2019 Sep 18;26:10-12. doi: 10.1016/j.mmcr.2019.09.003. eCollection 2019 Dec. Med Mycol Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31667051 Free PMC article.
-
A case of Talaromyces marneffei infection that required differentiation from Pneumocystis pneumonia.IDCases. 2022 Dec 1;31:e01654. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2022.e01654. eCollection 2023. IDCases. 2022. PMID: 36478666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chakrabarti A, Slavin MA, 2011. Endemic fungal infections in the Asia-Pacific region. Med Mycol 49: 337–344. - PubMed
-
- Yoshimura Y, Sakamoto Y, Lee K, Amano Y, Tachikawa N, 2016. Penicillium marneffei infection with beta-D-glucan elevation: a case report and literature review. Intern Med 55: 2503–2506. - PubMed
-
- Supparatpinyo K, Khamwan C, Baosoung V, Nelson KE, Sirisanthana T, 1994. Disseminated Penicillium marneffei infection in southeast Asia. Lancet 344: 110–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

