Obesity and pancreatitis
- PMID: 28719397
- PMCID: PMC6640854
- DOI: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000386
Obesity and pancreatitis
Abstract
Purpose of review: The obesity pandemic poses a unique set of problems for acute pancreatitis - both by increasing acute pancreatitis incidence, and worsening acute pancreatitis severity. This review explores these associations, underlying mechanisms, and potential therapies.
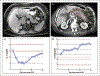
Recent findings: We review how the obesity associated increase in gallstones, surgical, and endoscopic interventions for obesity management, diabetes, and related medications such as incretin-based therapies and hypertriglyceridemia may increase the incidence of acute pancreatitis. The mechanism of how obesity may increase acute pancreatitis severity are discussed with a focus on cytokines, adipokines, damage-associated molecular patterns and unsaturated fatty acid-mediated lipotoxicity. The role of obesity in exacerbating pancreatic necrosis is discussed; focusing on obesity-associated pancreatic steatosis. We also discuss how peripancreatic fat necrosis worsens organ failure independent of pancreatic necrosis. Last, we discuss emerging therapies including choice of intravenous fluids and the use of lipase inhibitors which have shown promise during severe acute pancreatitis.
Summary: We discuss how obesity may contribute to increasing acute pancreatitis incidence, the role of lipolytic unsaturated fatty acid release in worsening acute pancreatitis, and potential approaches, including appropriate fluid management and lipase inhibition in improving acute pancreatitis outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
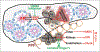
References
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, et al. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA 2006; 295:1549–1555. - PubMed
-
- Brown A, Young B, Morton J, et al. Are health related outcomes in acute pancreatitis improving? An analysis of national trends in the U.S. from 1997 to 2003. JOP 2008; 9:408–414. - PubMed
-
- Abu Hilal M, Armstrong T. The impact of obesity on the course and outcome of acute pancreatitis. Obes Surg 2008; 18:326–328. - PubMed
-
- Papachristou GI, Papachristou DJ, Avula H, et al. Obesity increases the severity of acute pancreatitis: performance of APACHE-O score and correlation with the inflammatory response. Pancreatology 2006; 6:279–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

