Lysyl Oxidase-like Protein LOXL2 Promotes Lung Metastasis of Breast Cancer
- PMID: 28720577
- PMCID: PMC5656180
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-3152
Lysyl Oxidase-like Protein LOXL2 Promotes Lung Metastasis of Breast Cancer
Erratum in
-
Correction: Lysyl Oxidase-like Protein LOXL2 Promotes Lung Metastasis of Breast Cancer.Cancer Res. 2023 Mar 15;83(6):974. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-0127. Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36919424 No abstract available.
Abstract
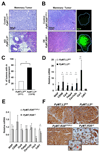
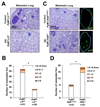
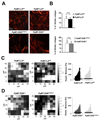
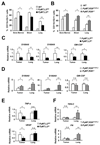
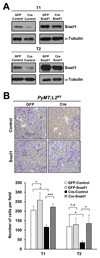
The lysyl oxidase-like protein LOXL2 has been suggested to contribute to tumor progression and metastasis, but in vivo evidence has been lacking. Here we provide functional evidence that LOXL2 is a key driver of breast cancer metastasis in two conditional transgenic mouse models of PyMT-induced breast cancer. LOXL2 ablation in mammary tumor cells dramatically decreased lung metastasis, whereas LOXL2 overexpression promoted metastatic tumor growth. LOXL2 depletion or overexpression in tumor cells does not affect extracellular matrix stiffness or organization in primary and metastatic tumors, implying a function for LOXL2 independent of its conventional role in extracellular matrix remodeling. In support of this likelihood, cellular and molecular analyses revealed an association of LOXL2 action with elevated levels of the EMT regulatory transcription factor Snail1 and expression of several cytokines that promote premetastatic niche formation. Taken together, our findings established a pathophysiologic role and new function for LOXL2 in breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res; 77(21); 5846-59. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

References
-
- Kim YM, Kim EC, Kim Y. The human lysyl oxidase-like 2 protein functions as an amine oxidase toward collagen and elastin. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38:145–9. - PubMed
-
- Barker HE, Cox TR, Erler JT. The rationale for targeting the LOX family in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:540–52. - PubMed
-
- Cano A, Santamaria PG, Moreno-Bueno G. LOXL2 in epithelial cell plasticity and tumor progression. Future Oncol. 2012;8:1095–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

