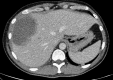
Persistent fever and right hypochondrium pain
- PMID: 28720605
- PMCID: PMC5535094
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2017-221254
Persistent fever and right hypochondrium pain
Keywords: hepatitis and other GI infections; infectious diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Stanley SL. Amoebiasis. The Lancet 2003;361:1025–34.doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12830-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lübbert C, Wiegand J, Karlas T. Therapy of liver abscesses. Viszeralmedizin 2014;30:334–41.doi:10.1159/000366579 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources