Influences of manganese on pubertal development
- PMID: 28720645
- PMCID: PMC5675006
- DOI: 10.1530/JOE-17-0237
Influences of manganese on pubertal development
Abstract
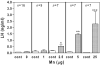
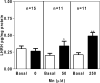
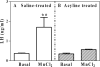
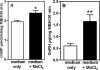
The onset of puberty is the result of complex neuroendocrine interactions within hypothalamic region of the brain, as well as from genetic and environmental influences. These interactions ultimately result in the increased synthesis and release of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH). Manganese (Mn) is an essential environmental element known for years to be involved in numerous mammalian physiological processes, including growth and reproductive function. Studies in recent years have shown the ability of Mn to cross the blood-brain barrier and act within the hypothalamus to influence the timing of puberty. This review will depict research showing the molecular and physiological actions of Mn in the control of prepubertal LHRH and discuss the potential for the element to cause either helpful or harmful outcomes on the developmental process depending upon the age and accumulation of Mn within the hypothalamus.
Keywords: hypothalamus; manganese; puberty.
© 2017 Society for Endocrinology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Aschner M, Aschner JL. Manganese transport across the blood brain barrier: relationship to iron homeostasis. Brain Research Bulletin. 1990;24:857–860. - PubMed
-
- Boyer PH, Shaw JH, Philips PH. Studies on manganese deficiency in the rat. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1942;143:417–425.
-
- Cardona-Gomez GP, Mendez P, Garcia-Segura LM. Synergistic interaction of estradiol and insulin-like growth factor-1 in the activation of P13K/Akt signaling in the adult rat hypothalamus. Molecular Brain Research. 2002;107:80–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

