Aortic Wall Inflammation Predicts Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Expansion, Rupture, and Need for Surgical Repair
- PMID: 28720724
- PMCID: PMC5571881
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.028433
Aortic Wall Inflammation Predicts Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Expansion, Rupture, and Need for Surgical Repair
Abstract
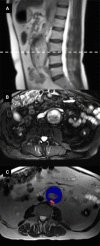
Background: Ultrasmall superparamagnetic particles of iron oxide (USPIO) detect cellular inflammation on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm, we assessed whether USPIO-enhanced MRI can predict aneurysm growth rates and clinical outcomes.
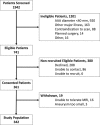
Methods: In a prospective multicenter open-label cohort study, 342 patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm (diameter ≥40 mm) were classified by the presence of USPIO enhancement and were monitored with serial ultrasound and clinical follow-up for ≥2 years. The primary end point was the composite of aneurysm rupture or repair.
Results: Participants (85% male, 73.1±7.2 years) had a baseline aneurysm diameter of 49.6±7.7 mm, and USPIO enhancement was identified in 146 (42.7%) participants, absent in 191 (55.8%), and indeterminant in 5 (1.5%). During follow-up (1005±280 days), 17 (5.0%) abdominal aortic aneurysm ruptures, 126 (36.8%) abdominal aortic aneurysm repairs, and 48 (14.0%) deaths occurred. Compared with those without uptake, patients with USPIO enhancement have increased rates of aneurysm expansion (3.1±2.5 versus 2.5±2.4 mm/year, P=0.0424), although this was not independent of current smoking habit (P=0.1993). Patients with USPIO enhancement had higher rates of aneurysm rupture or repair (47.3% versus 35.6%; 95% confidence intervals, 1.1-22.2; P=0.0308). This finding was similar for each component of rupture (6.8% versus 3.7%, P=0.1857) or repair (41.8% versus 32.5%, P=0.0782). USPIO enhancement was associated with reduced event-free survival for aneurysm rupture or repair (P=0.0275), all-cause mortality (P=0.0635), and aneurysm-related mortality (P=0.0590). Baseline abdominal aortic aneurysm diameter (P<0.0001) and current smoking habit (P=0.0446) also predicted the primary outcome, and the addition of USPIO enhancement to the multivariate model did not improve event prediction (c-statistic, 0.7935-0.7936).
Conclusions: USPIO-enhanced MRI is a novel approach to the identification of aortic wall cellular inflammation in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms and predicts the rate of aneurysm growth and clinical outcome. However, it does not provide independent prediction of aneurysm expansion or clinical outcomes in a model incorporating known clinical risk factors.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.isrctn.com. Unique identifier: ISRCTN76413758.
Keywords: MRI; abdominal aortic aneurysm; repair; rupture.
© 2017 The Authors.
Figures

Comment in
-
Letter by Zhu et al Regarding Article, "Aortic Wall Inflammation Predicts Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Expansion, Rupture, and Need for Surgical Repair".Circulation. 2018 Mar 20;137(12):1293-1294. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.030788. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 29555713 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Response to Letter Regarding Article, "Aortic Wall Inflammation Predicts Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Expansion, Rupture, and Need for Surgical Repair".Circulation. 2018 Mar 20;137(12):1295-1296. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.032344. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 29555714 No abstract available.
-
Predictions and insights for the abdominal aortic aneurysm.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Nov;10(11):5982-5984. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.10.15. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 30622768 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Aortic wall inflammation: a more accurate predictor of aneurysm expansion and aneurysm rupture risk than aortic diameter?J Thorac Dis. 2018 Nov;10(Suppl 33):S3865-S3866. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.09.36. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 30631500 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kent KC. Clinical practice. Abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2101–2108. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1401430. - PubMed
-
- Global Burden of Disease 2013 Mortality Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;385:117–171. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chaikof EL, Brewster DC, Dalman RL, Makaroun MS, Illig KA, Sicard GA, Timaran CH, Upchurch GR, Jr, Veith FJ Society for Vascular Surgery. The care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm: the Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines. J Vasc Surg. 2009;50(4 Suppl):S2–S49. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2009.07.002. - PubMed
-
- Moll FL, Powell JT, Fraedrich G, Verzini F, Haulon S, Waltham M, van Herwaarden JA, Holt PJ, van Keulen JW, Rantner B, Schlösser FJ, Setacci F, Ricco JB European Society for Vascular Surgery. Management of abdominal aortic aneurysms clinical practice guidelines of the European society for vascular surgery. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011;41(Suppl 1):S1–S58. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2010.09.011. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

