Obesity and inflammation: the linking mechanism and the complications
- PMID: 28721154
- PMCID: PMC5507106
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2016.58928
Obesity and inflammation: the linking mechanism and the complications
Abstract
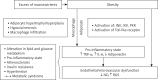
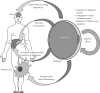
Obesity is the accumulation of abnormal or excessive fat that may interfere with the maintenance of an optimal state of health. The excess of macronutrients in the adipose tissues stimulates them to release inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor α and interleukin 6, and reduces production of adiponectin, predisposing to a pro-inflammatory state and oxidative stress. The increased level of interleukin 6 stimulates the liver to synthesize and secrete C-reactive protein. As a risk factor, inflammation is an imbedded mechanism of developed cardiovascular diseases including coagulation, atherosclerosis, metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and diabetes mellitus. It is also associated with development of non-cardiovascular diseases such as psoriasis, depression, cancer, and renal diseases. On the other hand, a reduced level of adiponectin, a significant predictor of cardiovascular mortality, is associated with impaired fasting glucose, leading to type-2 diabetes development, metabolic abnormalities, coronary artery calcification, and stroke. Finally, managing obesity can help reduce the risks of cardiovascular diseases and poor outcome via inhibiting inflammatory mechanisms.
Keywords: C reactive protein; adiponectin; inflammation; interleukin 6; linking mechanism; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Romano M. Inflammation resolution: does the bone marrow have a say? Am J Hematol. 2008;83:435–6. - PubMed
-
- Feuerstein GZ, Libby P, Mann DL. Inflammation – a new frontier in cardiac disease and therapeutics. In: Feuerstein GZ, Libby P, Mann DL, editors. Inflammation and cardiac diseases. Birkhäuser Basel; 2003. pp. 1–5.
-
- Seki H, Tani Y, Arita M. Omega-3 PUFA derived anti-inflammatory lipid mediator resolvin E1. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2009;89:126–30. - PubMed
-
- Bassuk SS, Rifai N, Ridker PM. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein: clinical importance. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2004;29:439–43. - PubMed
-
- Lafontan M. Fat cells: afferent and efferent messages define new approaches to treat obesity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004;45:119–46. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
