BRD4 inhibition for the treatment of pathological organ fibrosis
- PMID: 28721198
- PMCID: PMC5497817
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.11339.1
BRD4 inhibition for the treatment of pathological organ fibrosis
Abstract
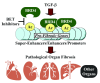
Fibrosis is defined as excess deposition of extracellular matrix, resulting in tissue scarring and organ dysfunction. It is estimated that 45% of deaths in the developed world are due to fibrosis-induced organ failure. Despite the well-accepted role of fibrosis in the pathogenesis of numerous diseases, there are only two US Food and Drug Administration-approved anti-fibrotic therapies, both of which are currently restricted to the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis. Thus, organ fibrosis represents a massive unmet medical need. Here, we review recent findings suggesting that an epigenetic regulatory protein, BRD4, is a nodal effector of organ fibrosis, and we highlight the potential of small-molecule BRD4 inhibitors for the treatment of diverse fibrotic diseases.
Keywords: BRD4; anti-fibrotic therapies; fibrotic diseases; organ fibrosis; small molecule BRD4 inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MSS and TAM declare that they have no competing interests. SMH is a scientific founder and shareholder of Tenava Therapeutics.No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

