Atrial fibrillation in a preterm newborn with structurally normal heart
- PMID: 28721223
- PMCID: PMC5509037
- DOI: 10.1093/omcr/omx010
Atrial fibrillation in a preterm newborn with structurally normal heart
Abstract
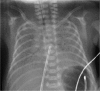
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a really uncommon arrhythmia in newborns. Here, we report the case of a 1-day-old infant who was recovered in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit for a twin-to-twin transfusion. The appearance of an unexpected AF was registered at his continuous electrocardiographic monitoring. Both chest X-ray and echocardiographic examination revealed the anomalous insertion of the tip of a central venous catheter (CVC) into the heart ('umbilical artery → inferior vena cava → right atrium → patent foramen ovale → left atrium'). AF ceased as soon as the CVC was extracted from the heart. The mechanical irritation of both atria caused by the malposition of the CVC might be the underlying mechanism responsible for the triggering of AF in this unique case report.
Figures
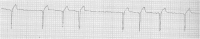

References
-
- Estlin EJ, Bennett MK, Skinner JR, Milligan DW, Wren C. Atrial fibrillation with neonatal pulmonary lymphangiectasia. Acta Paediatr 1998;87:1304–6. - PubMed
-
- Casado-Flores J, Barja J, Martino R, Serrano A, Valdivielso A. Complications of central venous catheterization in critically ill children. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2001;2:57–62. - PubMed
-
- Dodge KL, Lynch CA, Moore CL, Biroscak BJ, Evans LV. Use of ultrasound guidance improves central venous catheter insertion success rates among junior residents. J Ultrasound Med 2012;31:1519–26. - PubMed
-
- Obidi E, Toubas P, Sharma J. Atrial flutter in a premature infant with a structurally normal heart. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2006;19:113–4. - PubMed
-
- Polderman KH, Girbes AJ. Central venous catheter use. Part 1: mechanical complications. Intensive Care Med 2002;28:1–17. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

