ErbB activation signatures as potential biomarkers for anti-ErbB3 treatment in HNSCC
- PMID: 28723928
- PMCID: PMC5517012
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181356
ErbB activation signatures as potential biomarkers for anti-ErbB3 treatment in HNSCC
Abstract
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) accounts for 3-5% of all tumor types and remains an unmet medical need with only two targeted therapies approved to date. ErbB3 (HER3), the kinase-impaired member of the EGFR/ErbB family, has been implicated as a disease driver in a number of solid tumors, including a subset of HNSCC. Here we show that the molecular components required for ErbB3 activation, including its ligand neuregulin-1 (NRG1), are highly prevalent in HNSCC and that HER2, but not EGFR, is the major activating ErbB3 kinase partner. We demonstrate that cetuximab treatment primarily inhibits the ERK signaling pathway and KTN3379, an anti-ErbB3 monoclonal antibody, inhibits the AKT signaling pathway, and that dual ErbB receptor inhibition results in enhanced anti-tumor activity in HNSCC models. Surprisingly, we found that while NRG1 is required for ErbB3 activation, it was not sufficient to fully predict for KTN3379 activity. An evaluation of HNSCC patient samples demonstrated that NRG1 expression was significantly associated with expression of the EGFR ligands amphiregulin (AREG) and transforming growth factor α (TGFα). Furthermore, NRG1-positive HNSCC cell lines that secreted high levels of AREG and TGFα or contained high levels of EGFR homodimers (H11D) demonstrated a better response to KTN3379. Although ErbB3 and EGFR activation are uncoupled at the receptor level, their respective signaling pathways are linked through co-expression of their respective ligands. We propose that NRG1 expression and EGFR activation signatures may enrich for improved efficacy of anti-ErbB3 therapeutic mAb approaches when combined with EGFR-targeting therapies in HNSCC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


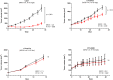

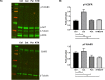

References
-
- Sacco AG, Cohen EE. Current Treatment Options for Recurrent or Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33: 3305–3313. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.62.0963 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arteaga CL, Engelman JA. ERBB Receptors: From Oncogene Discovery to Basic Science to Mechanism-Based Cancer Therapeutics. Cancer Cell. Elsevier Inc.; 2014;25: 282–303. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.02.025 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arteaga CL. ErbB-targeted therapeutic approaches in human cancer. Exp Cell Res. 2003;284: 122–130. doi: 10.1016/S0014-4827(02)00104-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shi F, Telesco SE, Liu Y, Radhakrishnan R, Lemmon MA. ErbB3/HER3 intracellular domain is competent to bind ATP and catalyze autophosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107: 7692–7697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1002753107 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jura N, Shan Y, Cao X, Shaw DE, Kuriyan J. Structural analysis of the catalytically inactive kinase domain of the human EGF receptor 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106: 21608–21613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912101106 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

