Effects of a structured education program on glycemic control in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 28724054
- PMCID: PMC10522068
- DOI: 10.1590/2359-3997000000278
Effects of a structured education program on glycemic control in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: Diabetes mellitus is associated with significant morbidity and mortality, and education is known to play a key role in managing this disease. This study addresses the effects of a structured education program (SEP) on self-care in subjects with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). The aim was to evaluate the effect of a SEP on glycemic control, knowledge, and skills associated with diabetes care in subjects with T1DM.
Subjects and methods: A total of 47 adults with T1DM were followed up for 20 months (32 participated in the SEP and 15 served as a control group). The SEP consisted of workshops, individualized care, 24-hour distant support, and a questionnaire assessing knowledge of diabetes care. Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels were measured before and after the SEP implementation.
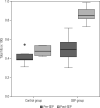
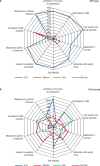
Results: Compared with pre-SEP levels, the mean HbA1c levels decreased by approximately 20% (21 mmol/mol) at 1 year, with a further 11% reduction (10 mmol/mol) observed 8 months later (p < 0.001). Knowledge about diabetes care increased by 37% between the pre-SEP and post-SEP questionnaires (p < 0.005).
Conclusion: Relevant improvements occurred after SEP activities. The sustained decrease in HbA1c levels and the overall increase in knowledge and confidence regarding diabetes care reinforce the importance, necessity, and positive outcomes of a SEP intervention in T1DM.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: no potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. The world health report 2002: reducing risks, promoting healthy life. World Health Organization, 2002.
-
- IDF. IDF Diabetes Atlas Seventh Edition. (2015). Available from: <http://www.idf.org/idf-diabetes-atlas-seventh-edition>. Access on: Feb. 16, 2016.
-
- National Audit Office. The management of adult diabetes services in the NHS. (2012). Available from: <https://www.nao.org.uk/report/the-management-of-adult-diabetes-services-...>. Access on: Feb. 16, 2016.
-
- Beeney LJ, Bakry AA, Dunn SM. Patient psychological and information needs when the diagnosis is diabetes. Patient Educ Couns. 1996;29(1):109-16. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
