Distribution of salicifoline in freeze-fixed stems of Magnolia kobus as observed by cryo-TOF-SIMS
- PMID: 28725003
- PMCID: PMC5517595
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-06444-0
Distribution of salicifoline in freeze-fixed stems of Magnolia kobus as observed by cryo-TOF-SIMS
Abstract
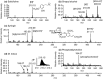
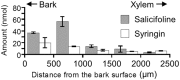
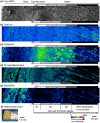
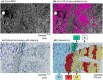
Alkaloids are basic nitrogen-containing chemicals that have important physiological and pharmacological characteristics. Many vascular plant species contain alkaloids, and their roles in planta are of interest. However, the detailed distribution of alkaloids remains unclear because of their low water solubility and low concentrations in plants. In this study, we visualized the distribution of salicifoline, a water-soluble quaternary ammonium alkaloid, in the freeze-fixed stems of Magnolia kobus by cryo time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry. Most of the salicifoline was distributed in living phloem tissues. In the xylem, salicifoline was detected in ray cells, lignifying wood fibres, and in vessels in the latest annual ring. The salicifoline distribution in the xylem varied with the cell wall formation stage. These results provide new insights into the storage, transportation, and role of the alkaloid salicifoline in M. kobus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Evans CR. Germination behavior of Magnolia grandiflora. Bot. Gaz. 1933;94:729–754. doi: 10.1086/334344. - DOI
-
- Aniszewski, T. Alkaloids - Secrets of Life. (Elsevier, 2007).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

