Isolation, biological evaluation and validated HPTLC-quantification of the marker constituent of the edible Saudi plant Sisymbrium irio L
- PMID: 28725148
- PMCID: PMC5506741
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2016.10.012
Isolation, biological evaluation and validated HPTLC-quantification of the marker constituent of the edible Saudi plant Sisymbrium irio L
Abstract
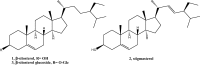
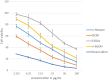
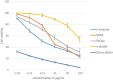
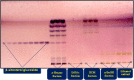
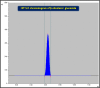
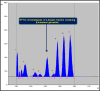
Phytochemical investigation and chromatographic purification of the n-hexane fraction of the aerial parts of the edible Saudi plant Sisymbrium irio led to the isolation of β-sitosterol (1), stigmasterol (2) and β-sitosterol-β-d-glucoside (3). The cytotoxic effects of the n-hexane, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate and n-butanol fractions were tested against three cancer cell lines viz., MCF-7, HCT-116 and HepG2, using the crystal violet staining (CVS) method, while the antibacterial activity against a number of pathogenic bacterial strains, was also estimated using the broth microdilution assay. The n-hexane fraction showed potent cytotoxic activities against all tested human cancer cell lines (IC50: 11.7-13.4 μg/mL), while the dichloromethane fraction was particularly potent against HCT-116 cells (IC50: 5.42 μg/mL). On the other hand, the n-hexane and EtOAc fractions demonstrated significant inhibitory activities against the Gram positive bacteria S. pyogenes and C. perfringens; and the Gram negative bacterium S. enteritidis. Our results warrant the therapeutic potential of S. irio as nutritional supplement to reduce the risk of contemporary diseases. Additionally, a validated high performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) method was developed for the quantitative analysis of biomarker β-sitosterol glucoside (isolated in high quantity) from the n-hexane fraction. The system was found to furnish a compact, sharp, symmetrical and high resolution band for β-sitosterol glucoside (Rf = 0.43 ± 0.002). The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) for β-sitosterol glucoside was found to be 21.84 and 66.18 ng band-1, respectively. β-sitosterol glucoside was found to be present only in n-hexane fraction (2.10 μg/mg of dried fraction) while it was absent in the other fractions of S. irio which validated the high cytotoxic and antibacterial activity of n-hexane fraction of S. irio.
Keywords: Antibacterial; Cytotoxic; Edible plants; HPTLC; Sisymbrium irio; β-sitosterol glucoside.
Figures


References
-
- Al-Jaber N. Phytochemical and biological studies of Sisymbrium irio L. growing in Saudi Arabia. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2011;15:345–350.
-
- Al-Qudah M.A., Abu Zarga M.H. Chemical constituents of Sisymbrium irio L. from Jordan. Nat. Prod. Res. 2010;24:448–456. - PubMed
-
- Awad A., Downie A., Fink C., Kim U. Dietary phytosterol inhibits the growth and metastasis of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells grown in SCID mice. Anticancer Res. 2000;20:821–824. - PubMed
-
- Conrad A., Biehler D., Nobis T., Richter H., Engels I., Biehler K., Frank U. Broad spectrum antibacterial activity of a mixture of isothiocyanates from nasturtium (Tropaeoli majoris herba) and horseradish (Armoraciae rusticanae radix) Drug Res. (Stuttg) 2013;63:65–68. - PubMed
-
- Di Sotto A., Vitalonem A., Nicoletti M., Piccin A., Mazzanti G. Pharmacological and phytochemical study on a Sisymbrium officinale Scop. extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010;127:731–736. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

