Alterations in adaptive immunity persist during long-duration spaceflight
- PMID: 28725716
- PMCID: PMC5515498
- DOI: 10.1038/npjmgrav.2015.13
Alterations in adaptive immunity persist during long-duration spaceflight
Abstract
Background: It is currently unknown whether immune system alterations persist during long-duration spaceflight. In this study various adaptive immune parameters were assessed in astronauts at three intervals during 6-month spaceflight on board the International Space Station (ISS).
Aims: To assess phenotypic and functional immune system alterations in astronauts participating in 6-month orbital spaceflight.
Methods: Blood was collected before, during, and after flight from 23 astronauts participating in 6-month ISS expeditions. In-flight samples were returned to Earth within 48 h of collection for immediate analysis. Assays included peripheral leukocyte distribution, T-cell function, virus-specific immunity, and mitogen-stimulated cytokine production profiles.
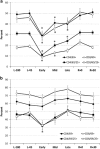
Results: Redistribution of leukocyte subsets occurred during flight, including an elevated white blood cell (WBC) count and alterations in CD8+ T-cell maturation. A reduction in general T-cell function (both CD4+ and CD8+) persisted for the duration of the 6-month spaceflights, with differential responses between mitogens suggesting an activation threshold shift. The percentage of CD4+ T cells capable of producing IL-2 was depressed after landing. Significant reductions in mitogen-stimulated production of IFNγ, IL-10, IL-5, TNFα, and IL-6 persisted during spaceflight. Following lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation, production of IL-10 was reduced, whereas IL-8 production was increased during flight.
Conclusions: The data indicated that immune alterations persist during long-duration spaceflight. This phenomenon, in the absence of appropriate countermeasures, has the potential to increase specific clinical risks for crewmembers during exploration-class deep space missions.
Conflict of interest statement
DP is a NASA Virologist and CS and BC are NASA Immunologists. All remaining authors possess positions (contractor scientist) at, or are funded by, NASA. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Chapes SK , Morrison DR , Guikema JA , Lewis ML , Spooner BS . Production and action of cytokines in space. Adv Space Res 1994; 14: 5–9. - PubMed
-
- Crucian BE , Stowe RP , Pierson DL , Sams CF . Immune system dysregulation following short- vs long-duration spaceflight. Aviat Space Environ Med 2008; 79: 835–843. - PubMed
-
- Sonnenfeld G , Miller ES . The role of cytokines in immune changes induced by spaceflight. J Leukoc Biol 1993; 54: 253–258. - PubMed
-
- Sonnenfeld G . Effect of space flight on cytokine production. Acta Astronaut 1994; 33: 143–147. - PubMed
-
- Morukov VB , Rykova MP , Antropova EN , Berendeeva TA , Ponomarev SA , Larina IM . Indicators of innate and adaptive immunity of cosmonauts after long-term space flight to international space station. Fiziol Cheloveka 2010; 36: 19–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

