SiMa Cells for a Serotype Specific and Sensitive Cell-Based Neutralization Test for Botulinum Toxin A and E
- PMID: 28726719
- PMCID: PMC5535177
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins9070230
SiMa Cells for a Serotype Specific and Sensitive Cell-Based Neutralization Test for Botulinum Toxin A and E
Abstract
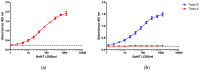
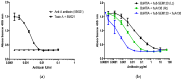
Botulinum toxins (BoNTs), of which there are seven serotypes, are among the most potent neurotoxins, with serotypes A, B and E causing human botulism. Antitoxins form the first line of treatment for botulism, and functional, highly sensitive in vitro methods for toxin neutralization are needed to replace the current in vivo methods used for determination of antitoxin potency. In this preliminary proof of concept study, we report the development of a neutralization test using the neuroblastoma SiMa cell line. The assay is serotype specific for either BoNT/A or BoNT/E, which both cleave unique sequences on SNAP-25 within SiMa cells. The end point is simple immunodetection of cleaved SNAP-25 from cell lysates with antibodies detecting only the newly exposed sequence on SNAP-25. Neutralizing antibodies prevent the toxin-induced cleavage of SNAP-25. The toxin neutralization assay, with an EC50 of ~2 mIU/mL determined with a standardized reference antiserum, is more sensitive than the mouse bioassays. Relevance was demonstrated with commercial and experimental antitoxins targeting different functional domains, and of known in vivo neutralizing activities. This is the first report describing a simple, specific, in vitro cell-based assay for the detection of neutralizing antibodies against BoNT/A and BoNT/E with a sensitivity exceeding that of the mouse bioassay.
Keywords: BoNT/A; BoNT/E; SNAP-25; SiMa cells; capture ELISA; cell-based assay; immunodetection; toxin neutralization test (TNT).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Pirazzini M., Azarnia Tehran D., Zanetti G., Megighian A., Scorzeto M., Fillo S., Shone C.C., Binz T., Rossetto O., Lista F., et al. Thioredoxin and its reductase are present on synaptic vesicles, and their inhibition prevents the paralysis induced by botulinum neurotoxins. Cell Rep. 2014;8:1870–1878. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.08.017. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

