Inflammatory pseudotumor of kidney: a challenging diagnostic entity
- PMID: 28727376
- PMCID: PMC5815552
- DOI: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2017.0063
Inflammatory pseudotumor of kidney: a challenging diagnostic entity
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None declared.
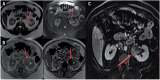
Figures


References
-
- Park SB, Cho KS, Kim JK, Lee JH, Jeong AK, Kwon WJ, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumor (myoblastic tumor) of the genitourinary tract. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;191:1255–1262. - PubMed
-
- Tazi K, Ehirchiou A, Karmouni T, Maazaz K, el Khadir K, Koutani A, et al. [Inflammatory pseudotumors of the kidney: a case report] Ann Urol (Paris). 2001;35:30–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
