Effects of a traditional Chinese medicine formula and its extraction on muscle fiber characteristics in finishing pigs, porcine cell proliferation and isoforms of myosin heavy chain gene expression in myocytes
- PMID: 28728382
- PMCID: PMC5666198
- DOI: 10.5713/ajas.16.0872
Effects of a traditional Chinese medicine formula and its extraction on muscle fiber characteristics in finishing pigs, porcine cell proliferation and isoforms of myosin heavy chain gene expression in myocytes
Abstract
Objective: This study evaluated the effects of a traditional Chinese medicine formula (TCMF) on muscle fiber characteristics in finishing pigs and the effects of the formula's extract (distilled water, ethyl acetate and petroleum ether extraction) on porcine cell proliferation and isoforms of myosin heavy chain (MyHC) gene expression in myocytes.
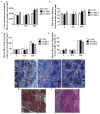
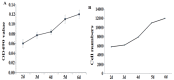
Methods: In a completely randomized design, ninety pigs were assigned to three diets with five replications per treatment and six pigs per pen. The diets included the basal diet (control group), TCMF1 (basal diet+2.5 g/kg TCMF) and TCMF2 (basal diet+5 g/kg TCMF). The psoas major muscle was obtained from pigs at the end of the experiment. Muscle fiber characteristics in the psoas major muscle were analyzed using myosin ATPase staining. Cell proliferation was measured using 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) dye and cytometry. Isoforms of MyHC gene expression were detected by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
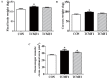
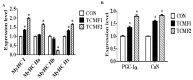
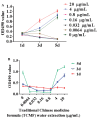
Results: The final body weight and carcass weight of finishing pigs were increased by TCMF1 (p<0.05), while the psoas major muscle cross-sectional area was increased by TCMF (p<0.05). The cross-sectional area and diameter of psoas major muscle fiber I, IIA, and IIB were increased by TCMF2 (p<0.05). The cross-sectional area and fiber diameter of psoas major muscle fiber IIA and IIB were increased by diet supplementation with TCMF1 (p<0.05). Psoas major muscle fiber IIA and IIB fiber density from the pigs fed the TCMF1 diet and the type IIB fiber density from the pigs fed the TCMF2 diet were lower compared to pigs fed the control diet (p<0.05). Pigs fed TCMF2 had a higher composition of type I fiber and a lower percentage of type IIB fiber in the psoas major muscle (p<0.05). The expression levels of MyHC I, MyHC IIa, and MyHC IIx mRNA increased and the amount of MyHC IIb mRNA decreased in the psoas major muscle from TCMF2, whereas MyHC I and MyHC IIx mRNA increased in the psoas major muscle from TCMF1 (p<0.05). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α and CaN mRNA expression in the psoas major muscle were up-regulated by TCMF (p<0.05). Porcine skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation was promoted by 4 μg/mL and 20 μg/mL TCMF water extraction (p<0.05). Both 1 μg/mL and 5 μg/mL of TCMF water extraction increased MyHC IIa, MyHC IIb, and MyHC IIx mRNA expression in porcine myocytes (p<0.05), while MyHC I mRNA expression in porcine myocytes was decreased by 5 μg/mL TCMF water extraction (p<0.05). Porcine myocyte MyHC I and MyHC IIx mRNA expression were increased, and MyHC IIa and MyHC IIb mRNA expression were down-regulated by 5 μg/mL TCMF ethyl acetate extraction (p<0.05). MyHC I and MyHC IIa mRNA expression in porcine myocytes were increased, and the MyHC IIb mRNA expression was decreased by 1 μg/mL TCMF ethyl acetate extraction (p<0.05). Four isoforms of MyHC mRNA expression in porcine myocytes were reduced by 5 μg/mL TCMF petroleum ether extraction (p<0.05). MyHC IIa mRNA expression in porcine myocytes increased and MyHC IIb mRNA expression decreased by 1 μg/mL in a TCMF petroleum ether extraction (p<0.05).
Conclusion: These results indicated that TCMF amplified the psoas major muscle cross-sectional area through changing muscle fiber characteristics in finishing pigs. This effect was confirmed as TCMF extraction promoted porcine cell proliferation and affected isoforms of MyHC gene expression in myocytes.
Keywords: Cell Proliferation; Muscle Fiber; Pigs; Traditional Chinese Medicine Formula.
Conflict of interest statement
We certify that there is no conflict of interest with any financial organization regarding the material discussed in the manuscript.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ractopamine-induced fiber type-specific gene expression in porcine skeletal muscles is independent of growth.J Anim Sci. 2020 Nov 1;98(11):skaa341. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa341. J Anim Sci. 2020. PMID: 33259597 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin heavy chain composition of different skeletal muscles in Large White and Meishan pigs.J Anim Sci. 2004 Jul;82(7):1931-41. doi: 10.2527/2004.8271931x. J Anim Sci. 2004. PMID: 15309939
-
Effect of myosin heavy chain composition of muscles on meat quality in Laiwu pigs and Duroc.Sci China C Life Sci. 2008 Feb;51(2):127-32. doi: 10.1007/s11427-008-0016-x. Sci China C Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18239890
-
Specialized cranial muscles: how different are they from limb and abdominal muscles?Cells Tissues Organs. 2003;174(1-2):73-86. doi: 10.1159/000070576. Cells Tissues Organs. 2003. PMID: 12784043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myopathies associated with myosin heavy chain mutations.Acta Myol. 2004 Sep;23(2):90-6. Acta Myol. 2004. PMID: 15605950 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of sheep slaughter age on myogenic characteristics in skeletal muscle satellite cells.Anim Biosci. 2022 Apr;35(4):614-623. doi: 10.5713/ab.21.0193. Epub 2022 Jan 3. Anim Biosci. 2022. PMID: 34991228 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of coated cysteamine hydrochloride on muscle fiber characteristics and amino acid composition of finishing pigs.Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2018 Oct 26;32(9):1430-1438. doi: 10.5713/ajas.18.0414. Print 2019 Sep. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2018. PMID: 30381744 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jeong DW, Choi YM, Lee SH, et al. Correlations of trained panel sensory values of cooked pork with fatty acid composition, muscle fiber type, and pork quality characteristics in Berkshire pigs. Meat Sci. 2010;86:607–15. - PubMed
-
- Lefaucheur L, Ecolan P, Plantard L, Gueguen N. New insights into muscle fiber types in the pig. J Histochem Cytochem. 2002;50:719–30. - PubMed
-
- Adamovic I, Vitorovic D, Blagojevic M, Nesic I, Brkic Z. Histological and histochemical properties of M. semitendinosus in German Landrace pigs at birth and market weight. Acta Vet-Beograd. 2014;64:319–26.
-
- Biswas AK, Keshri RC, Bisht GS. Effect of enrobing and antioxidants on quality characteristics of precooked pork patties under chilled and frozen storage conditions. Meat Sci. 2004;66:733–41. - PubMed
-
- Koreleski J, Swiatkiewicz S. Effect of dietary supplementation of vitamin E, antioxidants and a synthetic carotenoid on changes in chicken breast meat quality during storage. Ann Anim Sci. 2008;8:167–74.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

