Do high vs. low purchasers respond differently to a nonessential energy-dense food tax? Two-year evaluation of Mexico's 8% nonessential food tax
- PMID: 28729195
- PMCID: PMC5732875
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2017.07.009
Do high vs. low purchasers respond differently to a nonessential energy-dense food tax? Two-year evaluation of Mexico's 8% nonessential food tax
Abstract
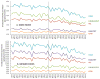
It is unclear whether response to a nonessential food tax varies across time or for high vs. low-consuming households. The objective is to examine whether the effect of Mexico's 2014 8% nonessential energy-dense foods tax increased in the second year post-implementation and whether it differentially affected households by pre-tax purchasing pattern. We used longitudinal data on Mexican household food purchases (n=6089 households) from 2012 to 2015. Households were classified based on median pre-tax purchases: low untaxed/low taxed ("low"), low untaxed/high taxed ("unhealthy"), high untaxed/low taxed ("healthy"), and high untaxed/high taxed ("high") purchasers. Fixed effects models tested whether observed post-tax purchases differed from the counterfactual, or what would have been expected based on pre-tax trends. Post-tax declines in the % taxed food purchases increased from -4.8% in year one to -7.4% in year two, yielding a 2-year mean decline of 6.0% beyond the counterfactual (p<0.01). Post-tax change in % taxed food purchases varied by pre-tax purchasing level. Healthy purchasers showed no post-tax change in % taxed food purchases beyond the counterfactual, while unhealthy, low and high purchasers decreased (-12.3%, -5.3% and -4.4%, respectively) (p<0.01). The positive effect of Mexico's junk food tax continued in the second year, and households with greater preferences for taxed foods showed a larger decline in taxed food purchases.
Keywords: Evaluation; Food taxes; Household purchases; Mexico.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures

References
-
- Barquera S, Campos-Nonato I, Hernández-Barrera L, Pedroza A, Rivera-Dommarco JA. Prevalence of obesity in Mexican adults 2000–2012. Salud publica de Mexico. 2013;55:S151–S60. - PubMed
-
- Barquera S, Hernandez-Barrera L, Tolentino ML, Espinosa J, Ng SW, Rivera JA, Popkin BM. Energy intake from beverages is increasing among Mexican adolescents and adults. J Nutr. 2008;138:2454–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

