Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients Discharged Home from an Emergency Department with AKI
- PMID: 28729384
- PMCID: PMC5544515
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.10431016
Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients Discharged Home from an Emergency Department with AKI
Abstract
Background and objectives: Patients discharged home from an emergency department with AKI are not well described. This study describes their characteristics and outcomes and compares these outcomes to two referent groups.
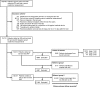
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: We conducted a population-based retrospective cohort study in Ontario, Canada from 2003 to 2012 of 6346 patients aged ≥40 years who were discharged from the emergency department with AKI (defined using serum creatinine values). We analyzed the risk of all-cause mortality, receipt of acute dialysis, and hospitalization within 30 days after discharge. We used propensity score methods to compare all-cause mortality to two referent groups. We matched 4379 discharged patients to 4379 patients who were hospitalized from the emergency department with similar AKI stage. We also matched 6188 discharged patients to 6188 patients who were discharged home from the emergency department with no AKI.
Results: There were 6346 emergency department discharges with AKI. The mean age was 69 years and 6012 (95%) had stage 1, 290 (5%) had stage 2, and 44 (0.7%) had stage 3 AKI. Within 30 days, 149 (2%) (AKI stage 1: 127 [2%]; stage 2: 15 [5%]; stage 3: seven [16%]) died, 22 (0.3%) received acute dialysis, and 1032 (16%) were hospitalized. An emergency department discharge versus hospitalization with AKI was associated with lower mortality (3% versus 12%; relative risk, 0.3; 95% confidence interval, 0.2 to 0.3). An emergency department discharge with AKI versus no AKI was associated with higher mortality (2% versus 1%; relative risk, 1.6; 95% confidence interval, 1.2 to 2.0).
Conclusions: Patients discharged home from the emergency department with AKI are at risk of poor 30-day outcomes. A better understanding of care in this at-risk population is warranted, as are testing strategies to improve care.
Keywords: Acute Kidney Injury; Aged; Canada; Confidence Intervals; Emergency Service, Hospital; Humans; Kidney Function Tests; Ontario; Patient Discharge; Propensity Score; Retrospective Studies; Risk; creatinine; hospitalization; renal dialysis.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Reconfiguring Health Care Delivery to Improve AKI Outcomes.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Aug 7;12(8):1203-1205. doi: 10.2215/CJN.05940617. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28729381 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Emergency Department Patients With Acute Kidney Injury: Appropriately Discharged but Inadequately Followed-Up?Acad Emerg Med. 2018 Jul;25(7):815-818. doi: 10.1111/acem.13379. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Acad Emerg Med. 2018. PMID: 29360211 No abstract available.
References
-
- Selby NM, Crowley L, Fluck RJ, McIntyre CW, Monaghan J, Lawson N, Kolhe NV: Use of electronic results reporting to diagnose and monitor AKI in hospitalized patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7: 533–540, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Porter CJ, Juurlink I, Bisset LH, Bavakunji R, Mehta RL, Devonald MA: A real-time electronic alert to improve detection of acute kidney injury in a large teaching hospital. Nephrol Dial Transplant 29: 1888–1893, 2014 - PubMed
-
- Garg AX, Kurz A, Sessler DI, Cuerden M, Robinson A, Mrkobrada M, Parikh CR, Mizera R, Jones PM, Tiboni M, Font A, Cegarra V, Gomez MF, Meyhoff CS, VanHelder T, Chan MT, Torres D, Parlow J, Clanchet Mde N, Amir M, Bidgoli SJ, Pasin L, Martinsen K, Malaga G, Myles P, Acedillo R, Roshanov PS, Walsh M, Dresser G, Kumar P, Fleischmann E, Villar JC, Painter T, Biccard B, Bergese S, Srinathan S, Cata JP, Chan V, Mehra B, Wijeysundera DN, Leslie K, Forget P, Whitlock R, Yusuf S, Devereaux PJ: Perioperative aspirin and clonidine and risk of acute kidney injury: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 312: 2254–2264, 2014 - PubMed
-
- Chertow GM, Burdick E, Honour M, Bonventre JV, Bates DW: Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay, and costs in hospitalized patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 16: 3365–3370, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Liangos O, Wald R, O’Bell JW, Price L, Pereira BJ, Jaber BL: Epidemiology and outcomes of acute renal failure in hospitalized patients: A national survey. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1: 43–51, 2006 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

