Bidirectional eukaryotic DNA replication is established by quasi-symmetrical helicase loading
- PMID: 28729513
- PMCID: PMC5608077
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aan0063
Bidirectional eukaryotic DNA replication is established by quasi-symmetrical helicase loading
Abstract
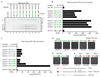
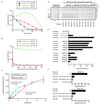
Bidirectional replication from eukaryotic DNA replication origins requires the loading of two ring-shaped minichromosome maintenance (MCM) helicases around DNA in opposite orientations. MCM loading is orchestrated by binding of the origin recognition complex (ORC) to DNA, but how ORC coordinates symmetrical MCM loading is unclear. We used natural budding yeast DNA replication origins and synthetic DNA sequences to show that efficient MCM loading requires binding of two ORC molecules to two ORC binding sites. The relative orientation of these sites, but not the distance between them, was found to be critical for MCM loading in vitro and origin function in vivo. We propose that quasi-symmetrical loading of individual MCM hexamers by ORC and directed MCM translocation into double hexamers acts as a unifying mechanism for the establishment of bidirectional replication in archaea and eukaryotes.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

