Trends in Hospitalizations for Serious Infections in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis in the US Between 1993 and 2013
- PMID: 28732148
- PMCID: PMC5776053
- DOI: 10.1002/acr.23328
Trends in Hospitalizations for Serious Infections in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis in the US Between 1993 and 2013
Abstract
Objective: The epidemiology of hospitalizations with infections among patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is unknown, despite an increase in RA treatments that confer a risk of infection.
Methods: We examined National Inpatient Sample data from 1993-2013. We identified hospitalizations among adults with RA, defined by International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification codes (714.xx) in any secondary diagnosis field. We evaluated 5 infections as the primary diagnosis: pneumonia, sepsis, urinary tract infection (UTI), skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs), and opportunistic infections (OIs). The primary outcome was the proportion of hospitalizations for each infection among all hospitalizations with a secondary diagnosis of RA.
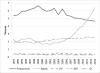
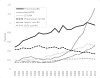
Results: There were 792,921 hospitalizations for infection with a secondary diagnosis of RA, with the rates increasing from 90 to 206 per 100,000 persons from 1993-2013. The proportion of hospitalizations decreased for pneumonia (from 5.4% to 4.6%), UTI (from 0.4% to 0.38%), and OIs (from 0.44% to 0.26%). The proportion of hospitalizations for SSTIs increased slightly (from 2.3% to 2.5%), while hospitalizations for sepsis more than tripled (from 1.9% to 6.4%).
Conclusion: Between 1993 and 2013, the proportion of hospitalizations for infections among RA patients appeared to decline for pneumonia and OIs, with a slight decrease in UTI, a slight increase in SSTIs, and a substantial increase in hospitalizations with sepsis. Our results are consistent with previous reports that the sensitivity of sepsis coding has increased over time.
© 2017, American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
References
-
- Doran MF, Crowson CS, Pond GR, O’Fallon WM, Gabriel SE. Frequency of infection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with controls: A population-based study. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:2287–93. - PubMed
-
- Yazici Y, Shi N, John A. Utilization of biologic agents in rheumatoid arthritis in the united states: Analysis of prescribing patterns in 16,752 newly diagnosed patients and patients new to biologic therapy. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2008;66:77–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

