Artemisia annua dried leaf tablets treated malaria resistant to ACT and i.v. artesunate: Case reports
- PMID: 28732806
- PMCID: PMC5547396
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2017.04.006
Artemisia annua dried leaf tablets treated malaria resistant to ACT and i.v. artesunate: Case reports
Abstract
Background: Dried leaf Artemisia annua (DLA) has shown efficacy against Plasmodium sp. in rodent studies and in small clinical trials. Rodent malaria also showed resiliency against the evolution of artemisinin drug resistance.
Purpose: This is a case report of a last resort treatment of patients with severe malaria who were responding neither to artemisinin combination therapy (ACT) nor i.v. artesunate.
Study design: Of many patients treated with ACTs and i.v. artesunate during the 6 mon study period, 18 did not respond and were subsequently treated with DLA Artemisia annua.
Methods: Patients were given a dose of 0.5g DLA per os, twice daily for 5d. Total adult delivered dose of artemisinin was 55mg. Dose was reduced for body weight under 30kg. Clinical symptoms, e.g. fever, coma etc., and parasite levels in thick blood smears were tracked. Patients were declared cured and released from hospital when parasites were microscopically undetectable and clinical symptoms fully subsided.
Results: All patients were previously treated with Coartem® provided through Santé Rurale (SANRU) and following the regimen prescribed by WHO. Of 18 ACT-resistant severe malaria cases compassionately treated with DLA, all fully recovered. Of the 18, this report details two pediatric cases.
Conclusions: Successful treatment of all 18 ACT-resistant cases suggests that DLA should be rapidly incorporated into the antimalarial regimen for Africa and possibly wherever else ACT resistance has emerged.
Keywords: ACT; Artemisia annua; Artemisinin drug resistance; Coartem; Dihydroartemisinin; Synergism.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
We wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Figures
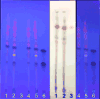
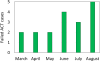
References
-
- Duke JA. Handbook of phytochemical constituents of GRAS herbs and other economic plants. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL: 2001. p. 70.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

