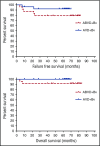
Five-year follow-up of brentuximab vedotin combined with ABVD or AVD for advanced-stage classical Hodgkin lymphoma
- PMID: 28733323
- PMCID: PMC5766843
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2017-05-784678
Five-year follow-up of brentuximab vedotin combined with ABVD or AVD for advanced-stage classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Abstract
Publisher's Note: There is an
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Brentuximab: is it time for a new "B" in ABVD?Blood. 2017 Sep 14;130(11):1281-1282. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-08-798553. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28912294 No abstract available.
References
-
- Merli F, Luminari S, Gobbi PG, et al. . Long-term results of the HD2000 trial comparing ABVD versus BEACOPP versus COPP-EBV-CAD in untreated patients with advanced Hodgkin lymphoma: a study by Fondazione Italiana Linfomi. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(11):1175-1181. - PubMed
-
- Carde P, Karrasch M, Fortpied C, et al. . Eight cycles of ABVD versus four cycles of BEACOPPescalated plus four cycles of BEACOPPbaseline in stage III to IV, International Prognostic Score ≥ 3, high-risk Hodgkin lymphoma: first results of the phase III EORTC 20012 Intergroup Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(17):2028-2036. - PubMed
-
- Radford J, Illidge T, Counsell N, et al. . Results of a trial of PET-directed therapy for early-stage Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(17):1598-1607. - PubMed
-
- Connors JM. Risk assessment in the management of newly diagnosed classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2015;125(11):1693-1702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical