A case series of pediatric seymour fractures related to hoverboards: Increasing trend with changing lifestyle
- PMID: 28735119
- PMCID: PMC5522954
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2017.06.058
A case series of pediatric seymour fractures related to hoverboards: Increasing trend with changing lifestyle
Abstract
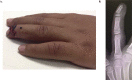
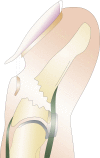
Background: Several recreational activities such as roller skating, skateboarding, and scooter riding create the risk for hand injuries, which are the fourth most commonly injured body part in relation to their use. Seymour first identified a specific pattern of digit injury as an open fracture affecting the distal phalangeal physis associated with nail avulsion from the eponychial fold. In this article, we report a series of Seymour fractures associated with misuse of the newly emerging recreational/transportation vehicle, the hoverboard.
Method: The study includes a retrospective chart review of patients who presented to a tertiary hospital between December 2015 and October 2016 with a Seymour fracture caused while operating a hoverboard.
Results: A total of 13 patients were treated for Seymour fractures. The majority were male patients, and the group had a mean age of 10.3 years (±2.21). The affected digits were primarily the middle and ring fingers of the non-dominant hand. The injury mechanism reported by patients or families indicated that the child was operating the hoverboard in a sitting position with the hands grasping the wheel rim parts.
Conclusion: We report a case series of a fracture pattern resulting from the improper/unsafe use of a hoverboard. This type of fracture occurs with a tremendous load of energy. Although improper use was a factor, design fault also plays a role in causing the injury. Parent awareness and supervision are important to prevent such injuries.
Keywords: Fracture; Hand; Hoverboard; Injury; Seymour.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Cornwall R., Ricchetti E.T. Pediatric phalanx fractures: unique challenges and pitfalls. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2006;445:146–156. - PubMed
-
- Galano G.J., Vitale M.A., Kessler M.W., Hyman J.E., Vitale M.G. The most frequent traumatic orthopaedic injuries from a national pediatric inpatient population. J. Pediatr. Orthoped. 2005;25(1):39–44. - PubMed
-
- Bhende M.S., Dandrea L.A., Davis H.W. Hand injuries in children presenting to a pediatric emergency department. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1993;22(10):1519–1523. - PubMed
-
- Abzug J.M., Kozin S.H. Seymour fractures. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2013;38(11):2267–2270. quiz 70. - PubMed
-
- Seymour N. Juxta-epiphysial fracture of the terminal phalanx of the finger. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. Vol. 1966;48(2):347–349. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

