The serine/threonine protein phosphatase 2A controls autoimmunity
- PMID: 28736280
- PMCID: PMC5776067
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2017.07.012
The serine/threonine protein phosphatase 2A controls autoimmunity
Abstract
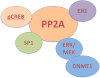
Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) is the first serine/threonine phosphatase recognized to contribute to human and murine lupus immunopathology. PP2A expression in SLE is controlled both epigenetically and genetically, and it is increased in patients with SLE, which contributes to decreased IL-2 production, decreased CD3ζ and increased FcRγ expression on the surface of T cells, increased CREMα expression, hypomethylation of genes associated with SLE pathogenesis, and increased IL-17 production. β regulatory subunit of PP2A regulates IL-2 deprivation-induced T cell death and is decreased in SLE patients. A mouse overexpressing PP2Ac in T cells displays peripheral granulocytosis, elevated IL-17 production, and develops glomerulonephritis when challenged. A mouse which lacks PP2Ac only in regulatory T cells develops severe autoimmunity and multiorgan inflammation because of loss of restraint on mTORC1 and inability of Foxp3+ cells to regulate conventional T cells. Targeting PP2A in T cell subsets may be therapeutic for SLE and other autoimmune diseases.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Shi Y. Serine/threonine phosphatases: mechanism through structure. Cell. 2009;139:468–484. - PubMed
-
- Lambrecht C, Haesen D, Sents W, Ivanova E, Janssens V. Structure, regulation, and pharmacological modulation of PP2A phosphatases. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013;1053:283–305. - PubMed
-
- Janssens V, Longin S, Goris J. PP2A holoenzyme assembly: in cauda venenum (the sting is in the tail) Trends Biochem Sci. 2008;33:113–121. - PubMed
-
- Kong M, Fox CJ, Mu J, Solt L, Xu A, Cinalli RM, Birnbaum MJ, Lindsten T, Thompson CB. The PP2A-associated protein alpha4 is an essential inhibitor of apoptosis. Science. 2004;306:695–698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

