Brain Natriuretic Peptide Is a Marker of Fluid Overload in Incident Hemodialysis Patients
- PMID: 28736562
- PMCID: PMC5511993
- DOI: 10.1159/000471815
Brain Natriuretic Peptide Is a Marker of Fluid Overload in Incident Hemodialysis Patients
Abstract
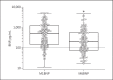
Background/aims: Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) is secreted by cardiomyocytes under stretch condition. High blood levels are associated with decreased patient survival in heart failure patients and in hemodialysis (HD) patients. We report the monthly BNP change in the first months of HD therapy in incident patients and its relationship with fluid removal and cardiac history (CH).
Methods: All patients starting HD therapy in our unit from May 2008 to December 2012 were retrospectively analyzed. Every month (M1 to M6), BNP was assessed before a midweek dialysis session. CH, monthly pre- and postdialysis blood pressure, and postdialysis body weight were collected.
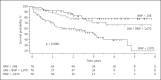
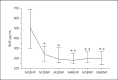
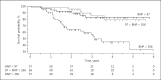
Results: A total of 236 patients were included in the analysis. The median BNP at HD start was 593 (175-1,433) pg/mL, with a significant difference between CH- and CH+ patients (291 vs. 731 pg/mL, p < 0.0001). Mortality was significantly higher in patients in the higher BNP tertile. BNP decreased significantly between M1 and M2 and then plateaued. The BNP change between M1 and M2 and between M1 and M6 was significantly correlated with the initial fluid removal. Applying stepwise multiple regression, the BNP change between M1 and M2 was significantly and independently related to fluid removal. The BNP level at M6 was also related to patient survival.
Conclusions: We confirm that in incident HD patients, BNP level is related to fluid excess and cardiac status. The BNP decrease in the first months of HD therapy is related to fluid excess correction. BNP appears as an important tool to evaluate hydration status correction after HD onset.
Keywords: Brain natriuretic peptide; Fluid overload; Hemodialysis; Incident patients; Survival.
Figures


References
-
- Joffy S, Rosner MH. Natriuretic peptides in ESRD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005;46:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Anand IS, Fisher LD, Chiang YT, Latini R, Masson S, Maggioni AP, Glazer RD, Tognoni G, Cohn JN, Val-HeFT Investigators Changes in brain natriuretic peptide and norepinephrine over time and mortality and morbidity in the Valsartan Heart Failure Trial (Val-HeFT) Circulation. 2003;107:1278–1283. - PubMed
-
- Zoccali C, Mallamaci F, Benedetto F, Tripepi G, Parlongo S, Cataliotti A, Cutrupi S, Giacone G, Bellanuova I, Cottini E, Malatino L, Creed Investigators Cardiac natriuretic peptides are related to left ventricular mass and function and predict mortality in dialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12:1508–1515. - PubMed
-
- Chazot C, Vo-Van C, Deleaval P, Lorriaux C, Hurot JM, Mayor B, Jean G. Predialysis systolic blood pressure evolution in incident hemodialysis patients: effects of the dry weight method and prognostic value. Blood Purif. 2012;33:275–283. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
