Platycodon grandiflorus Root Extract Improves Learning and Memory by Enhancing Synaptogenesis in Mice Hippocampus
- PMID: 28737698
- PMCID: PMC5537907
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9070794
Platycodon grandiflorus Root Extract Improves Learning and Memory by Enhancing Synaptogenesis in Mice Hippocampus
Abstract
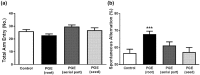
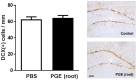
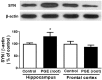
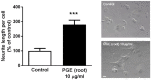
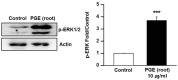
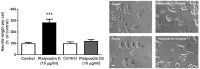
Platycodon grandiflorus (Jacq.) A.DC. (PG) has long been used as an ingredient of foods and is known to have beneficial effects on cognitive functions as well. The present study examined the effect of each PG extract (PGE) from root, aerial part, and seeds on cognitive functions in mice. Changes in spatial learning and memory using a Y-maze test, and markers of adult hippocampal neurogenesis and synaptogenesis were examined. Moreover, changes in neuritogenesis and activation of the ERK1/2 pathway were investigated. Results indicated that mice administered PGE (root) showed increased spontaneous alternation in the Y-maze test and synaptogenesis in the hippocampus. In addition, PGE (root) and platycodin D, the major bioactive compound from the PG root, significantly stimulated neuritic outgrowth by phosphorylation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway in vitro. These results indicate that the PGE (root), containing platycodin D, enhances cognitive function through synaptogenesis via activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway.
Keywords: Platycodon grandiflorus; cognition; neuritogenesis; platycodin D; synaptogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Liu D., Diorio J., Day J.C., Francis D.D., Meaney M.J. Maternal care, hippocampal synaptogenesis and cognitive development in rats. Nat. Neurosci. 2000;3:799–806. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

