Regulation and Modulation of Human DNA Polymerase δ Activity and Function
- PMID: 28737709
- PMCID: PMC5541323
- DOI: 10.3390/genes8070190
Regulation and Modulation of Human DNA Polymerase δ Activity and Function
Abstract
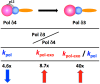
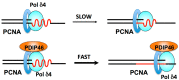
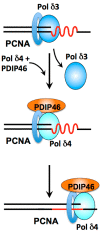
This review focuses on the regulation and modulation of human DNA polymerase δ (Pol δ). The emphasis is on the mechanisms that regulate the activity and properties of Pol δ in DNA repair and replication. The areas covered are the degradation of the p12 subunit of Pol δ, which converts it from a heterotetramer (Pol δ4) to a heterotrimer (Pol δ3), in response to DNA damage and also during the cell cycle. The biochemical mechanisms that lead to degradation of p12 are reviewed, as well as the properties of Pol δ4 and Pol δ3 that provide insights into their functions in DNA replication and repair. The second focus of the review involves the functions of two Pol δ binding proteins, polymerase delta interaction protein 46 (PDIP46) and polymerase delta interaction protein 38 (PDIP38), both of which are multi-functional proteins. PDIP46 is a novel activator of Pol δ4, and the impact of this function is discussed in relation to its potential roles in DNA replication. Several new models for the roles of Pol δ3 and Pol δ4 in leading and lagging strand DNA synthesis that integrate a role for PDIP46 are presented. PDIP38 has multiple cellular localizations including the mitochondria, the spliceosomes and the nucleus. It has been implicated in a number of cellular functions, including the regulation of specialized DNA polymerases, mitosis, the DNA damage response, mouse double minute 2 homolog (Mdm2) alternative splicing and the regulation of the NADPH oxidase 4 (Nox4).
Keywords: DNA damage response; DNA polymerase δ; DNA replication; E3 ligases; PDIP38; PDIP46; Poldip2; Poldip3; cell cycle; enzyme regulation; p12 subunit.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Brutlag D., Kornberg A. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. 36. A proofreading function for the 3′ leads to 5′ exonuclease activity in deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases. J. Biol. Chem. 1972;247:241–248. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

