Rapidly inducible Cas9 and DSB-ddPCR to probe editing kinetics
- PMID: 28737741
- PMCID: PMC5730411
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.4368
Rapidly inducible Cas9 and DSB-ddPCR to probe editing kinetics
Abstract
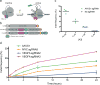
We developed a chemically inducible Cas9 (ciCas9) and a droplet digital PCR assay for double-strand breaks (DSB-ddPCR) to investigate the kinetics of Cas9-mediated generation and repair of DSBs in cells. ciCas9 is a rapidly activated, single-component Cas9 variant engineered by replacing the protein's REC2 domain with the BCL-xL protein and fusing an interacting BH3 peptide to the C terminus. ciCas9 can be tunably activated by a compound that disrupts the BCL-xL-BH3 interaction within minutes. DSB-ddPCR demonstrates time-resolved, highly quantitative, and targeted measurement of DSBs. Combining these tools facilitated an unprecedented exploration of the kinetics of Cas9-mediated DNA cleavage and repair. We find that sgRNAs targeting different sites generally induce cleavage within minutes and repair within 1 or 2 h. However, we observe distinct kinetic profiles, even for proximal sites, and this suggests that target sequence and chromatin state modulate cleavage and repair kinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Richardson CD, Ray GJ, DeWitt MA, Curie GL, Corn JE. Enhancing homology-directed genome editing by catalytically active and inactive CRISPR-Cas9 using asymmetric donor DNA. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016;34:339–344. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

