A systematic review of the effectiveness of task-specific rehabilitation interventions for improving independent sitting and standing function in spinal cord injury
- PMID: 28738740
- PMCID: PMC6055957
- DOI: 10.1080/10790268.2017.1350340
A systematic review of the effectiveness of task-specific rehabilitation interventions for improving independent sitting and standing function in spinal cord injury
Abstract
Context: Impaired balance function after a spinal cord injury (SCI) hinders performance of daily activities.
Objective: To assess the evidence on the effectiveness of task-specific training on sitting and standing function in individuals with SCI across the continuum of care.
Methods: A systematic search was conducted on literature published to June 2016 using people (acute or chronic SCI), task-specific interventions compared to conventional physical therapy, and outcome (sitting or standing balance function). The PEDro scale was used to investigate the susceptibility to bias and trial quality of the randomized controlled trials (RCTs). A standardized mean difference (SMD) was conducted to investigate the effect size for interventions with sitting or standing balance outcomes.
Results: Nineteen articles were identified; three RCTs, two prospective controlled trials, one cross-over study, nine pre-post studies and four prospective cohort studies. RCT and cross-over studies were rated from 6 to 8 indicating good quality on the PEDro scale. The SMD of task-specific interventions in sitting compared to active and inactive (no training) control groups was -0.09 (95% CI: -0.663 to 0.488) and 0.39 (95% CI: -0.165 to 0.937) respectively, indicating that the addition of task-specific exercises did not affect sit and reach test performance significantly. Similarly, the addition of BWS training did not significantly affect BBS compared to conventional physical therapy -0.36 (95% CI: -0.840 to 0.113). Task-specific interventions reported in uncontrolled trials revealed positive effects on sitting and standing balance function.
Conclusion: Few RCT studies provided balance outcomes, and those that were evaluated indicate negligible effect sizes. Given the importance of balance control underpinning all aspects of daily activities, there is a need for further research to evaluate specific features of training interventions to improve both sitting and standing balance function in SCI.
Keywords: Gait; Postural balance; Rehabilitation; Review; Spinal cord injuries.
Figures
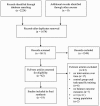

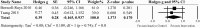

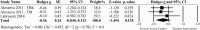

References
-
- Horak FB, Macpherson JM.. Postural Orientation and Equilibrium. Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2011.
-
- Winter DA. Human balance and posture control during standing and walking. Gait Posture 1995;3(4):193–214. doi: 10.1016/0966-6362(96)82849-9 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
