The critical phase for visual control of human walking over complex terrain
- PMID: 28739912
- PMCID: PMC5558990
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1611699114
The critical phase for visual control of human walking over complex terrain
Abstract
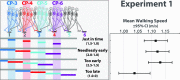
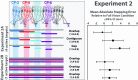
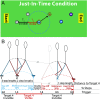
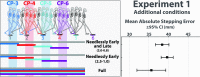
To walk efficiently over complex terrain, humans must use vision to tailor their gait to the upcoming ground surface without interfering with the exploitation of passive mechanical forces. We propose that walkers use visual information to initialize the mechanical state of the body before the beginning of each step so the resulting ballistic trajectory of the walker's center-of-mass will facilitate stepping on target footholds. Using a precision stepping task and synchronizing target visibility to the gait cycle, we empirically validated two predictions derived from this strategy: (1) Walkers must have information about upcoming footholds during the second half of the preceding step, and (2) foot placement is guided by information about the position of the target foothold relative to the preceding base of support. We conclude that active and passive modes of control work synergistically to allow walkers to negotiate complex terrain with efficiency, stability, and precision.
Keywords: biomechanics; foot placement; human locomotion; inverted pendulum; visual control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Bernstein N. Pergamon Press; New York: 1967. The coordination and regulation of movements.
-
- Schaal S, Atkeson CG, Sternad D. One-handed juggling: A dynamical approach to a rhythmic movement task. J Mot Behav. 1996;28:165–183. - PubMed
-
- Rossignol S, Dubuc R, Gossard J-P. Dynamic sensorimotor interactions in locomotion. Physiol Rev. 2006;86:89–154. - PubMed
-
- Cavagna GA, Margaria R. Mechanics of walking. J Appl Physiol. 1966;21:271–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

