An integrated strategy by using target tissue metabolomics biomarkers as pharmacodynamic surrogate indices to screen antipyretic components of Qingkaikling injection
- PMID: 28740079
- PMCID: PMC5524955
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-05812-0
An integrated strategy by using target tissue metabolomics biomarkers as pharmacodynamic surrogate indices to screen antipyretic components of Qingkaikling injection
Abstract
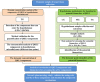
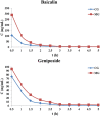
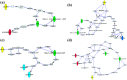
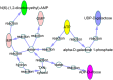
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) treatment can be valuable therapeutic strategies. However, the active components and action mechanisms that account for its therapeutic effects remain elusive. Based on the hypothesis that the components of a formula which exert effect would be measurable in target tissue, a target tissue metabolomics-based strategy was proposed for screening of antipyretic components in Qingkaikling injection (QKLI). First, we detected the components of QKLI which could reach its target tissue (hypothalamus) by determining the hypothalamus microdialysate and discovered that only baicalin and geniposide could be detected. Then, by conducting hypothalamus metabolomics studies, 14 metabolites were screened as the potential biomarkers that related to the antipyretic mechanisms of QKLI and were used as its pharmacodynamic surrogate indices. Subsequently, the dynamic concentration of baicalin and geniposide in hypothalamus microdialysates and biomarkers in hypothalamus were measured and correlated with each other. The results indicated that only baicalin shown a good correlation with these biomarkers. Finally, a network pharmacology approach was established to validate the antipyretic activity of baicalin and the results elucidated its antipyretic mechanisms as well. The integrated strategy proposed here provided a powerful means for identifying active components and mechanisms contributing to pharmacological effects of TCM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
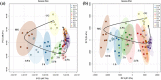
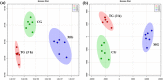
 ), MG (
), MG ( ), and TG at 3 h (
), and TG at 3 h ( ). (a) At positive ion mode. (b) At negative ion mode.
). (a) At positive ion mode. (b) At negative ion mode.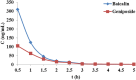
Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Modeling to Study the Antipyretic Effect of Qingkailing Injection on Pyrexia Model Rats.Molecules. 2016 Mar 7;21(3):317. doi: 10.3390/molecules21030317. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 26959005 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma metabolomics combined with lipidomics profiling reveals the potential antipyretic mechanisms of Qingkailing injection in a rat model.Chem Biol Interact. 2016 Jul 25;254:24-33. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2016.05.022. Epub 2016 May 18. Chem Biol Interact. 2016. PMID: 27208622
-
Serum and urine metabolomics based on UPLC-Q-TOF/MS reveals the antipyretic mechanism of Reduning injection in a rat model.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Mar 25;250:112429. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112429. Epub 2019 Dec 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31812644
-
The Progress of Metabolomics Study in Traditional Chinese Medicine Research.Am J Chin Med. 2015;43(7):1281-310. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X15500731. Epub 2015 Oct 18. Am J Chin Med. 2015. PMID: 26477800 Review.
-
Metabolomics: towards understanding traditional Chinese medicine.Planta Med. 2010 Dec;76(17):2026-35. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1250542. Epub 2010 Nov 5. Planta Med. 2010. PMID: 21058239 Review.
Cited by
-
Fever and Antipyretic Supported by Traditional Chinese Medicine: A Multi-Pathway Regulation.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 22;12:583279. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.583279. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33828481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the Mechanism of Xiaochaihu Granules in Alleviating Yeast-Induced Fever Based on Network Analysis and Experimental Validation.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 8;17(4):475. doi: 10.3390/ph17040475. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675434 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on Main Symptoms of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Improved by Traditional Chinese Medicine.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 11;11:556885. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.556885. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33013395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of aristolochic acid Ι nephrotoxicity in mice via 1H NMR quantitative metabolomics and network pharmacology approaches.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023 Mar 25;12(2):282-295. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfad020. eCollection 2023 Apr. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023. PMID: 37125334 Free PMC article.
-
Huangjia Ruangan Granule Inhibits Inflammation in a Rat Model with Liver Fibrosis by Regulating TNF/MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jul 30;2022:8105306. doi: 10.1155/2022/8105306. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35942372 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

