Tumor microenvironment dual-responsive core-shell nanoparticles with hyaluronic acid-shield for efficient co-delivery of doxorubicin and plasmid DNA
- PMID: 28740384
- PMCID: PMC5503489
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S134378
Tumor microenvironment dual-responsive core-shell nanoparticles with hyaluronic acid-shield for efficient co-delivery of doxorubicin and plasmid DNA
Abstract
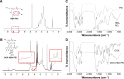
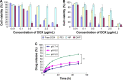
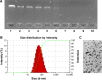
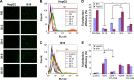
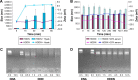
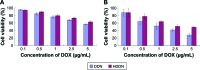
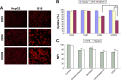
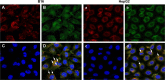
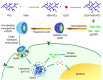
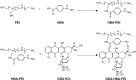
As the tumor microenvironment (TME) develops, it is critical to take the alterations of pH value, reduction and various enzymes of the TME into consideration when constructing the desirable co-delivery systems. Herein, TME pH and enzyme dual-responsive core-shell nanoparticles were prepared for the efficient co-delivery of chemotherapy drug and plasmid DNA (pDNA). A novel pH-responsive, positively charged drug loading material, doxorubicin (DOX)-4-hydrazinobenzoic acid (HBA)-polyethyleneimine (PEI) conjugate (DOX-HBA-PEI, DHP), was synthesized to fabricate positively charged polyion complex inner core DHP/DNA nanoparticles (DDN). Hyaluronic acid (HA) was an enzyme-responsive shell which could protect the core and enhance the co-delivery efficiency through CD44-mediated endocytosis. The HA-shielded pH and enzyme dual-responsive nanoparticles (HDDN) were spherical with narrow distribution. The particle size of HDDN was 148.3±3.88 nm and the zeta potential was changed to negative (-18.1±2.03 mV), which led to decreased cytotoxicity. The cumulative release of DOX from DHP at pH 5.0 (66.4%) was higher than that at pH 7.4 (30.1%), which indicated the pH sensitivity of DHP. The transfection efficiency of HDDN in 10% serum was equal to that in the absence of serum, while the transfection of DDN was significantly decreased in the presence of 10% serum. Furthermore, cellular uptake studies and co-localization assay showed that HDDN were internalized effectively through CD44-mediated endocytosis in the tumor cells. The efficient co-delivery of DOX and pEGFP was confirmed by fluorescent image taken by laser confocal microscope. It can be concluded that TME dual-responsive HA-shielded core-shell nanoparticles could be considered as a promising platform for the co-delivery of chemotherapy drug and pDNA.
Keywords: CD44 targeted; co-delivery; core–shell nanoparticles; hyaluronic acid; pH sensitive.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reduction-sensitive CD44 receptor-targeted hyaluronic acid derivative micelles for doxorubicin delivery.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Jul 26;13:4361-4378. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S165359. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30100720 Free PMC article.
-
CD44-Targeted Hyaluronic Acid-Coated Redox-Responsive Hyperbranched Poly(amido amine)/Plasmid DNA Ternary Nanoassemblies for Efficient Gene Delivery.Bioconjug Chem. 2016 Jul 20;27(7):1723-36. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00240. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Bioconjug Chem. 2016. PMID: 27311558
-
Dual pH-responsive multifunctional nanoparticles for targeted treatment of breast cancer by combining immunotherapy and chemotherapy.Acta Biomater. 2018 Jan 15;66:310-324. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.11.010. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29129789
-
Hyaluronic acid-based nanoplatforms for Doxorubicin: A review of stimuli-responsive carriers, co-delivery and resistance suppression.Carbohydr Polym. 2021 Nov 15;272:118491. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118491. Epub 2021 Jul 27. Carbohydr Polym. 2021. PMID: 34420747 Review.
-
Hyaluronic acid-functionalized nanomedicines for CD44-receptors-mediated targeted cancer therapy: A review of selective targetability and biodistribution to tumor microenvironment.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 May;308(Pt 2):142486. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.142486. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40139601 Review.
Cited by
-
Quercetin and doxorubicin co-delivery using mesoporous silica nanoparticles enhance the efficacy of gastric carcinoma chemotherapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Sep 6;13:5113-5126. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S170862. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30233175 Free PMC article.
-
Polyethyleneimine (PEI) as a Polymer-Based Co-Delivery System for Breast Cancer Therapy.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2022 Apr 8;14:71-83. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S350403. eCollection 2022. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2022. PMID: 35422657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyaluronic Acid-Conjugated with Hyperbranched Chlorin e6 Using Disulfide Linkage and Its Nanophotosensitizer for Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer Cells.Materials (Basel). 2019 Sep 21;12(19):3080. doi: 10.3390/ma12193080. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31546620 Free PMC article.
-
The sustained PGE2 release matrix improves neovascularization and skeletal muscle regeneration in a hindlimb ischemia model.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Feb 24;20(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01301-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35209908 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

