Role of TIM-4 in exosome-dependent entry of HIV-1 into human immune cells
- PMID: 28740388
- PMCID: PMC5505621
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S132762
Role of TIM-4 in exosome-dependent entry of HIV-1 into human immune cells
Abstract
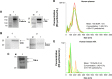
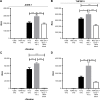
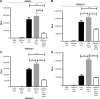
Exosomes, 30-200 nm nanostructures secreted from donor cells and internalized by recipient cells, can play an important role in the cellular entry of some viruses. These microvesicles are actively secreted into various body fluids, including blood, urine, saliva, cerebrospinal fluid, and breast milk. We successfully isolated exosomes from human breast milk and plasma. The size and concentration of purified exosomes were measured by nanoparticle tracking, while Western blotting confirmed the presence of the exosomal-associated proteins CD9 and CD63, clathrin, and T cell immunoglobulin and mucin proteins (TIMs). Through viral infection assays, we determined that HIV-1 utilizes an exosome-dependent mechanism for entry into human immune cells. The virus contains high amounts of phosphatidylserine (PtdSer) and may bind PtdSer receptors, such as TIMs. This mechanism is supported by our findings that exosomes from multiple sources increased HIV-1 entry into T cells and macrophages, and viral entry was potently blocked with anti-TIM-4 antibodies.
Keywords: HIV-1; T cell immunoglobulin and mucin proteins; exosomes; nanoparticle tracking analysis; phosphatidylserine.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neural stem cell-derived exosomes mediate viral entry.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014 Oct 21;9:4893-7. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S70999. eCollection 2014. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 25364247 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Human and Murine T-Cell Immunoglobulin Mucin Domain 4 (TIM-4) IgV Domain Residues Critical for Ebola Virus Entry.J Virol. 2016 Jun 10;90(13):6097-6111. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00100-16. Print 2016 Jul 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27122575 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of phosphatidylserine exposed on the viral envelope and cell membrane in HIV-1 replication.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Oct 21;17(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0452-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 31638994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the phosphatidylserine receptor TIM-1 in enveloped-virus entry.J Virol. 2013 Aug;87(15):8327-41. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01025-13. Epub 2013 May 22. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23698310 Free PMC article.
-
Seminal exosomes and HIV-1 transmission.Andrologia. 2018 Dec;50(11):e13220. doi: 10.1111/and.13220. Andrologia. 2018. PMID: 30569645 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Examination of Feline Coronavirus and Canine Coronavirus Effects on Extracellular Vesicles Acquired from A-72 Canine Fibrosarcoma Cell Line.Vet Sci. 2025 May 15;12(5):477. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12050477. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40431570 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on Microglial-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis and Composition.Pathogens. 2019 Dec 14;8(4):297. doi: 10.3390/pathogens8040297. Pathogens. 2019. PMID: 31847332 Free PMC article.
-
The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes.Science. 2020 Feb 7;367(6478):eaau6977. doi: 10.1126/science.aau6977. Science. 2020. PMID: 32029601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function and characteristics of TIM‑4 in immune regulation and disease (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2023 Feb;51(2):10. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5213. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Int J Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36524355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral Membrane Fusion Proteins and RNA Sorting Mechanisms for the Molecular Delivery by Exosomes.Cells. 2021 Nov 5;10(11):3043. doi: 10.3390/cells10113043. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831268 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

