Chemoradiation therapy with docetaxel in elderly patients with stage II/III esophageal cancer: A phase 2 trial
- PMID: 28740892
- PMCID: PMC5514160
- DOI: 10.1016/j.adro.2016.07.002
Chemoradiation therapy with docetaxel in elderly patients with stage II/III esophageal cancer: A phase 2 trial
Abstract
Purpose: The most effective treatments in elderly patients with esophageal cancer remain a subject of debate. This multicenter phase 2 study was designed to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of chemoradiation therapy (CRT) with docetaxel (DTX) in elderly patients with stage II/III (non-T4) esophageal cancer.
Methods and materials: Patients ≥70 years of age with clinical stage II/III esophageal cancer received DTX at a weekly dose of 10 mg/m2 during 6 consecutive weeks and concurrent radiation therapy (60 Gy in 30 fractions). The primary endpoint was the 2-year survival rate, and the required number of enrolled patients was 37.
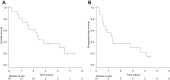
Results: Between July 2008 and January 2011, 16 patients were enrolled. The study was prematurely closed because of slow accrual. Characteristics of the patients were as follows: median age, 77 years (range, 73-81); performance status 0/1, 4/12; and clinical stage IIA/IIB/III, 3/4/9. Of the 16 patients, 14 (87.5%) completed the CRT. The 2-year survival rate was 62.5% (90% confidence interval [CI], 42.5-82.5). The median survival time was 27.7 months (95% CI, 23.3-32.2 months) and the median progression-free survival was 15.2 months (95% CI, 5.4-25.0 months). Seven patients achieved complete response, resulting in a complete response rate of 43.8% (95% CI, 19.8-70.1). Grade 3 or higher acute toxicities included esophagitis (31.3%), anorexia (12.5%), leukopenia (6.3%), neutropenia (6.3%), thrombocytopenia (6.3%), mucositis (6.3%), and infection (6.3%). Grade 3 or higher late toxicities included esophagitis (12.5%), pleural effusion (12.5%), pneumonitis (6.3%), and pericardial effusion (6.3%).
Conclusions: CRT with DTX might be a treatment option for elderly patients with stage II/III esophageal cancer, particularly for patients who are medically unfit for surgery or cisplatin-containing therapy. However, further improvements of this therapy are required to decrease the incidence of esophagitis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Feasibility of definitive chemoradiation therapy with nedaplatin and 5-fluorouracil in elderly patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective study.Adv Radiat Oncol. 2018 Mar 1;3(3):305-313. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2018.02.010. eCollection 2018 Jul-Sep. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30197939 Free PMC article.
-
Phase II study of chemoradiotherapy with 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin for Stage II-III esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: JCOG trial (JCOG 9906).Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011 Nov 1;81(3):684-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.06.033. Epub 2010 Oct 6. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011. PMID: 20932658 Clinical Trial.
-
Definitive chemoradiation therapy with docetaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil (DCF-R) in advanced esophageal cancer: a phase 2 trial (KDOG 0501-P2).Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014 Jul 15;89(4):872-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.03.030. Epub 2014 May 24. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014. PMID: 24867539 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase II study of concurrent chemoradiotherapy at the dose of 50.4 Gy with elective nodal irradiation for Stage II-III esophageal carcinoma.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2013 Jun;43(6):608-15. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyt048. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23585687 Clinical Trial.
-
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: preclinical and early clinical data.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2004 Feb;18(1):41-53. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8588(03)00138-2. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2004. PMID: 15005280 Review.
Cited by
-
Concurrent chemoradiation therapy tailored to the older adults with esophageal cancer: state of the art and the future.Clin Interv Aging. 2018 Nov 8;13:2275-2287. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S179014. eCollection 2018. Clin Interv Aging. 2018. PMID: 30519009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retrospective Analysis of Definitive Chemoradiotherapy With FOLFOX in Patients With Esophageal Cancer Intolerant to Cisplatin.In Vivo. 2024 Mar-Apr;38(2):761-766. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13499. In Vivo. 2024. PMID: 38418117 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of definitive chemoradiation therapy with nedaplatin and 5-fluorouracil in elderly patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective study.Adv Radiat Oncol. 2018 Mar 1;3(3):305-313. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2018.02.010. eCollection 2018 Jul-Sep. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30197939 Free PMC article.
-
Does chemoradiotherapy benefit elderly patients with esophageal squamous cell cancer? A propensity-score matched analysis on multicenter data (3JECROG R-03A).BMC Cancer. 2020 Jan 15;20(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6461-z. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31941487 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of involved-field intensity-modulated radiotherapy combined with S-1 vs radiotherapy alone for elderly patients with esophageal cancer.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Jul 26;10(21):7365-7375. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i21.7365. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 36157997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkin D.M., Bray F., Ferlay J. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- The Editorial Board of the Cancer Statistics in Japan. Cancer Statistics in Japan 2007 Foundation for Promotion of Cancer Research.
-
- Bonavina L., Incarbone R., Saino G. Clinical outcome and survival after esophagectomy for carcinoma in elderly patients. Dis Esophagus. 2003;16:90–93. - PubMed
-
- Steyerberg E.W., Neville B., Weeks J.C. Referral patterns, treatment choices, and outcomes in locoregional esophageal cancer: A population-based analysis of elderly patients. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:2389–2396. - PubMed
-
- Kinugasa S., Tachibana M., Yoshimura H. Esophageal resection in elderly esophageal carcinoma patients: Improvement in postoperative complications. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;71:414–418. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials