Hypofractionated image guided radiation therapy followed by prostate seed implant boost for men with newly diagnosed intermediate and high risk adenocarcinoma of the prostate: Preliminary results of a phase 2 prospective study
- PMID: 28740903
- PMCID: PMC5514232
- DOI: 10.1016/j.adro.2016.08.005
Hypofractionated image guided radiation therapy followed by prostate seed implant boost for men with newly diagnosed intermediate and high risk adenocarcinoma of the prostate: Preliminary results of a phase 2 prospective study
Abstract
Purpose: A phase 2 protocol was designed and implemented to assess the toxicity and efficacy of hypofractionated image guided intensity modulated radiation therapy (IG-IMRT) combined with low-dose rate 103Pd prostate seed implant for treatment of localized intermediate- and high-risk adenocarcinoma of the prostate.
Methods and materials: This is a report of an interim analysis on 24 patients enrolled on an institutional review board-approved phase 2 single-institution study of patients with intermediate- and high-risk adenocarcinoma of the prostate. The median pretreatment prostate-specific antigen level was 8.15 ng/mL. The median Gleason score was 4 + 3 = 7 (range, 3 + 4 = 7 - 4 + 4 = 8), and the median T stage was T2a. Of the 24 patients, 4 (17%) were high-risk patients as defined by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network criteria, version 2016. The treatment consisted of 2465 cGy in 493 cGy/fraction of IG-IMRT to the prostate and seminal vesicles. This was followed by a 103Pd transperineal prostate implant boost (prescribed dose to 90% of the prostate volume of 100 Gy) using intraoperative planning. Five patients received neoadjuvant, concurrent, and adjuvant androgen deprivation therapy.
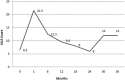
Results: The median follow-up was 18 months (range, 1-42 months). The median nadir prostate-specific antigen was 0.5 ng/mL and time to nadir was 16 months. There was 1 biochemical failure associated with distant metastatic disease without local failure. Toxicity (acute or late) higher than grade 3 was not observed. There was a single instance of late grade 3 genitourinary toxicity secondary to hematuria 2 years and 7 months after radiation treatment. There were no other grade 3 gastrointestinal or genitourinary toxicities.
Conclusions: Early results on the toxicity and efficacy of the combination of hypofractionated IG-IMRT and low-dose-rate brachytherapy boost are favorable. Longer follow-up is needed to confirm safety and effectiveness.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early outcomes of high-dose-rate brachytherapy combined with ultra-hypofractionated radiation in higher-risk prostate cancer.Brachytherapy. 2021 Nov-Dec;20(6):1099-1106. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2021.08.006. Epub 2021 Sep 26. Brachytherapy. 2021. PMID: 34588146
-
Acute genitourinary toxicity after high-dose-rate (HDR) brachytherapy combined with hypofractionated external-beam radiation therapy for localized prostate cancer: correlation between the urethral dose in HDR brachytherapy and the severity of acute genitourinary toxicity.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005 Oct 1;63(2):463-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.11.041. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. PMID: 16168838
-
Hypofractionated concomitant intensity-modulated radiotherapy boost for high-risk prostate cancer: late toxicity.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012 Feb 1;82(2):898-905. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.11.003. Epub 2011 Jan 14. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012. PMID: 21237581 Clinical Trial.
-
Acute genitourinary toxicity after high dose rate (HDR) brachytherapy combined with hypofractionated external-beam radiation therapy for localized prostate cancer: Second analysis to determine the correlation between the urethral dose in HDR brachytherapy and the severity of acute genitourinary toxicity.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005 Oct 1;63(2):472-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.02.015. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. PMID: 16168839
-
Preliminary toxicity and prostate-specific antigen response of a Phase I/II trial of neoadjuvant hormonal therapy, 103Pd brachytherapy, and three-dimensional conformal external beam irradiation in the treatment of locally advanced prostate cancer.Brachytherapy. 2002;1(1):2-10. doi: 10.1016/s1538-4721(02)00006-5. Brachytherapy. 2002. PMID: 15062181 Review.
References
-
- National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference on the Management of Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer. Bethesda, MD, June 15-17, 1987. NCI Monogr. 1988;(7):1–174. - PubMed
-
- Kuban D.A., Tucker S.L., Dong L. Long-term results of the M. D. Anderson randomized dose-escalation trial for prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70:67–74. - PubMed
-
- Peeters S.T., Heemsbergen W.D., Koper P.C. Dose-response in radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer: Results of the Dutch multicenter randomized phase III trial comparing 68 Gy of radiotherapy with 78 Gy. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1990–1996. - PubMed
-
- Pollack A., Zagars G.K., Starkschall G. Prostate cancer radiation dose response: Results of the M. D. Anderson phase III randomized trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;53:1097–1105. - PubMed
-
- Zietman A.L., DeSilvio M.L., Slater J.D. Comparison of conventional-dose vs high-dose conformal radiation therapy in clinically localized adenocarcinoma of the prostate: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2005;294:1233–1239. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources