Effects of co-exposure to atrazine and ethanol on the oxidative damage of kidney and liver in Wistar rats
- PMID: 28741978
- PMCID: PMC6446176
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2017.1351373
Effects of co-exposure to atrazine and ethanol on the oxidative damage of kidney and liver in Wistar rats
Abstract
Both ethanol (EtoH) and atrazine (ATZ) have hepatic and nephro-toxic effects in rats. In the present study, the toxicity of EtoH (5 g kg-1) on the kidney and liver in the absence or in the presence of different doses of ATZ (50, 100, 300 mg kg-1) was evaluated after 21 days in rats. Results showed that the mixture effects on catalase and superoxide dismutase activities were more severe in both tissues compared to EtoH alone, especially as the dose of ATZ was increased. Hepatic malondialdehyde level (an index of lipid peroxidation) was increased from 20.32% in the EtoH +50 mg kg-1 ATZ-treated rats to 34% in the EtoH +300 mg kg-1 ATZ-treated rats compared to the EtoH values. Renal malondialdehyde values remain as high as 81% in the EtoH-treated rats and the different combine exposure groups. Furthermore, as the dose of ATZ in the mixture was increased, serum uric acid level increased compared to the EtoH values. When the EtoH +300 mg kg-1 ATZ-animals were pretreated with curcumin (an antioxidant), the histopathological changes and peroxidative damages in both tissues were blocked. The exposure of EtoH-treated rats to ATZ enhanced renal and hepatic peroxidative damages in rats.
Keywords: Atrazine; curcumin; ethanol; histopathological damage; kidney; liver; malondialdehyde.
Figures
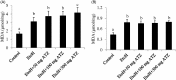

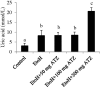



References
-
- Zeljezic D, Garaj-Vrhovac V, Perkovic P.. Evaluation of DNA damage induced by atrazine and atrazine-based herbicide in human lymphocytes in vitro using a comet and DNA diffusion assay. Toxicol In Vitro. 2006;20:923–935. - PubMed
-
- Frank A.The economics of atrazine. Int J Occup Environ Health. 2007;13:37–45. - PubMed
-
- Goldman LR.Atrazine, simazine and cynazine: notice of initiation of special review. Fed Regist. 1994;59:60412–60443.
-
- Abarikwu SO, Farombi EO.. Evaluating the reproductive toxicities and tumor-promoting properties of the chloro-s-triazine herbicide, atrazine in the vertebrates’ male and female animals In: Justin AU, editor. Advances in environmental research. New York, NY: Nova Science Publishers; 2012. p. 459–486.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
