Predicting the risk of Lyme borreliosis after a tick bite, using a structural equation model
- PMID: 28742149
- PMCID: PMC5524385
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181807
Predicting the risk of Lyme borreliosis after a tick bite, using a structural equation model
Abstract
Background: Understanding and quantification of the risk of Lyme borreliosis after a tick bite can aid development of prevention strategies against Lyme borreliosis.
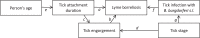
Methods: We used 3,525 single tick bite reports from three large prospective studies on the transmission risk of tick-borne pathogens to humans, with 50 reports of Lyme borreliosis during the follow-up period, among 1,973 reports with known outcome. A structural equation model was applied to estimate the risk of Lyme borreliosis after a tick bite, and quantify the influence of: developmental stage of the tick, detection of Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. DNA in the tick by PCR, tick engorgement, patient-estimated duration of tick attachment, and patient age.
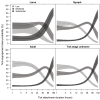
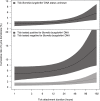
Results: The overall risk of developing Lyme borreliosis after a tick bite was 2.6% (95%CI 1.4-5.1). The risk increased with: - Tick engorgement: 1.4% (95%CI 0.7%-2.3%) for low engorgement to 5.5% (95%CI 2.8%-9.2%) for substantially engorged ticks;- Rising patient-estimated tick attachment duration: 2.0% (95%CI 1.3%-2.8%) after <12 hours, to 5.2% (95%CI 3.0%-8.9%) after ≥4 days;- Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. DNA in ticks: 6.7% (95%CI 3.6%-13.5%), versus 1.4% (95%CI 0.7%-2.9%) when ticks tested negative.The highest observed risk of Lyme borreliosis was 14.4% (95%CI 6.8%-24.6%) after one tick bite of a substantially engorged tick that tested positive for Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. DNA, which corresponds to one new case of Lyme borreliosis per 7 (95%CI 4-15) of such tick bites.
Conclusions: An individual's risk of Lyme borreliosis after a tick bite can be predicted with tick engorgement, patient-estimated duration of tick attachment, and detection of Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. DNA in the tick.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Stanek G, Wormser GP, Gray J, Strle F. Lyme borreliosis. Lancet. 2012;379(9814):461–73. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60103-7 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hubalek Z. Epidemiology of lyme borreliosis. Current problems in dermatology. 2009;37:31–50. doi: 10.1159/000213069 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gray JS, Stanek G. Risk assessment in Lyme borreliosis. Zentralblatt fur Bakteriologie: international journal of medical microbiology. 1998;287(3):175–6. . - PubMed
-
- Jaenson TG. The epidemiology of lyme borreliosis. Parasitol Today. 1991;7(2):39–45. . - PubMed
-
- Gray JS, Kahl O, Robertson JN, Daniel M, Estrada-Pena A, Gettinby G, et al. Lyme borreliosis habitat assessment. Zentralblatt fur Bakteriologie: international journal of medical microbiology. 1998;287(3):211–28. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

