The role of supplementary environmental surveillance to complement acute flaccid paralysis surveillance for wild poliovirus in Pakistan - 2011-2013
- PMID: 28742803
- PMCID: PMC5526532
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180608
The role of supplementary environmental surveillance to complement acute flaccid paralysis surveillance for wild poliovirus in Pakistan - 2011-2013
Abstract
Background: More than 99% of poliovirus infections are non-paralytic and therefore, not detected by acute flaccid paralysis (AFP) surveillance. Environmental surveillance (ES) can detect circulating polioviruses from sewage without relying on clinical presentation. With extensive ES and continued circulation of polioviruses, Pakistan presents a unique opportunity to quantify the impact of ES as a supplement to AFP surveillance on overall completeness and timeliness of poliovirus detection.
Methods: Genetic, geographic and temporal data were obtained for all wild poliovirus (WPV) isolates detected in Pakistan from January 2011 through December 2013. We used viral genetics to assess gaps in AFP surveillance and ES as measured by detection of 'orphan viruses' (≥1.5% different in VP1 capsid nucleotide sequence). We compared preceding detection of closely related circulating isolates (≥99% identity) detected by AFP surveillance or ES to determine which surveillance system first detected circulation before the presentation of each polio case.
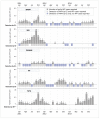
Findings: A total of 1,127 WPV isolates were detected by AFP surveillance and ES in Pakistan from 2011-2013. AFP surveillance and ES combined exhibited fewer gaps (i.e., % orphan viruses) in detection than AFP surveillance alone (3.3% vs. 7.7%, respectively). ES detected circulation before AFP surveillance in nearly 60% of polio cases (200 of 346). For polio cases reported from provinces conducting ES, ES detected circulation nearly four months sooner on average (117.6 days) than did AFP surveillance.
Interpretation: Our findings suggest ES in Pakistan is providing earlier, more sensitive detection of wild polioviruses than AFP surveillance alone. Overall, targeted ES through strategic selection of sites has important implications in the eradication endgame strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Morales M, Tangermann RH, Wassilak SG. Progress Toward Polio Eradication—Worldwide, 2015–2016. MMWR Morbidity and mortality weekly report. 2016;65(18):470–3. Epub 2016/05/14. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6518a4 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Global Polio Eradication Initiative, Geneva, Switzerland2017 [18 Jan 2017]. Available from: http://polioeradication.org/polio-today/polio-now/.
-
- Initiative GPE. Polio Eradication & Endgame Strategic Plan 2013–2018. 2013.
-
- Poliomyelitis: intensification of the global eradication initiative World Health Organization, 2012.
-
- Sutter RW, Kew OM, Cochi SL, Aylward RB. Chapter 28—Poliovirus vaccine—live Offit Paul A., Plotkin Stanley A., Orenstein Walter A. Vaccines (Sixth Edition). London: W.B. Saunders; 2013. p. 598–645.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

