Fluorescence and Sensing Applications of Graphene Oxide and Graphene Quantum Dots: A Review
- PMID: 28742956
- PMCID: PMC5915373
- DOI: 10.1002/asia.201700814
Fluorescence and Sensing Applications of Graphene Oxide and Graphene Quantum Dots: A Review
Abstract
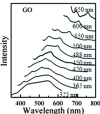
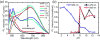
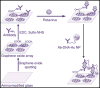
Graphene oxide and graphene quantum dots are attractive fluorophores that are inexpensive, nontoxic, photostable, water-soluble, biocompatible, and environmentally friendly. They find extensive applications in fluorescent biosensors and chemosensors, in which they serve as either fluorophores or quenchers. As fluorophores, they display tunable photoluminescence emission and the "giant red-edge effect". As quenchers, they exhibit a remarkable quenching efficiency through either electron transfer or Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) process. In this review, the origin of fluorescence and the mechanism of excitation wavelength-dependent fluorescence of graphene oxide and graphene quantum dots are discussed. Sensor design strategies based on graphene oxide and graphene quantum dots are presented. The applications of these sensors in health care, the environment, agriculture, and food safety are highlighted.
Keywords: biosensors; fluorescence; graphene; quantum dots; sensors.
© 2017 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Huang HM, Li ZB, She JC, Wang WL. J Appl Phys. 2012;111:054317.
- Mathkar A, Tozier D, Cox P, Ong PJ, Galande C, Balakrishnan K, Reddy ALM, Ajayan PM. J Phys Chem Lett. 2012;3:986–991. - PubMed
-
- Zhu SJ, Zhang JH, Qiao CY, Tang SJ, Li YF, Yuan WJ, Li B, Tian L, Liu F, Hu R, Gao HN, Wei HT, Zhang H, Sun HC, Yang B. Chem Commun. 2011;47:6858–6860. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

