Non-adherence to medication regimens among older African-American adults
- PMID: 28743244
- PMCID: PMC5526276
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-017-0558-5
Non-adherence to medication regimens among older African-American adults
Abstract
Background: Despite concerns about racial differences on adherence to prescribed medication rigimens among older adults, current information about nonadherence among underserved elderly African Americans with co-morbidities is limited. This study examines the association between adherence to drug regimens and an array of medication-related factors, including polypharmacy, medication regimen complexity, use of Potentially Inappropriate Medications (PIM), and knowledge about the therapeutic purpose and instructions of medication use.
Methods: Four-hundred African Americans, aged 65 years and older, were recruited from South Los Angeles. Structured, face-to-face interviews and visual inspection of participants' medications were conducted. From the medication container labels, information including strength of the drug, expiration date, instructions, and special warnings were recorded. The Medication Regimen Complexity Index (MRCI) was measured to quantify multiple features of drug regimen complexity. The Beers Criteria was used to measure the PIM use.
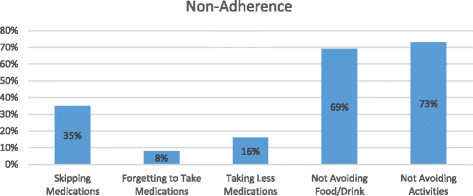
Results: Participants reported taking an average of 5.7 prescription drugs. Over 56% could not identify the purpose of at least one of their medications. Only two-thirds knew dosage regimen of their medications. Thirty-five percent of participants indicated that they purposely had skipped taking at least one of their medications within last three days. Only 8% of participants admitted that they forgot to take their medications. The results of multivariate analysis showed that co-payment for drugs, memory deficits, MRCI, and medication-related knowledge were all associated with adherence to dosage regimen of medications. Participants with a higher level of knowledge about therapeutic purpose and knowledge about dosage regimen of their medications were seven times (CI: 4.2-10.8) more likely to adhere to frequency and dose of medications. Participants with a low complexity index were two times (CI: 1.1-3.9) more likely to adhere to the dosage regimen of their medications, compared with participants with high drug regimen complexity index.
Conclusions: While other studies have documented that non-adherence remains an important issue among older adults, our study shows that for underserved elderly African Americans, these issues are particularly striking. A periodic comprehensive assessment of all medications that they use remains a critical initial step to identify medication related issues. Assessment of their disease and medication related knowledge (e.g., therapeutic purposes, side-effects, special instructions, etc.) and their ability to follow complicated medication regimens and modification of their drug regimens requires inter-professional collaboration.
Keywords: African-Americans; Medication knowledge; Medications; Non-adherence; Regimen complexity.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Charles R. Drew University of Medicine and Science Institutional Review Board. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical