Hypertension prevalence and influence of basal metabolic rate on blood pressure among adult students in Bangladesh
- PMID: 28743284
- PMCID: PMC5526296
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-017-4617-9
Hypertension prevalence and influence of basal metabolic rate on blood pressure among adult students in Bangladesh
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: BMC Public Health, Vol. 18.BMC Public Health. 2017 Sep 22;17(1):736. doi: 10.1186/s12889-017-4709-6. BMC Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28938882 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Hypertension is a global health issue and is currently increasing at rapid pace in South Asian countries including Bangladesh. Although, some studies on hypertension have been conducted in Bangladesh, there is a lack of scientific evidence in the adult student population that was missing from the previous and recent national cross-sectional studies. Moreover, the specific risk factors of hypertension in the Bangladeshi adults still need to be investigated. This study was conducted to estimate hypertension prevalence among adult students in Bangladesh and to test the hypothesis of Luke et al. (Hypertension 43:555-560, 2004) that basal metabolic rate (BMR) and blood pressure are positively associated independent of body size.
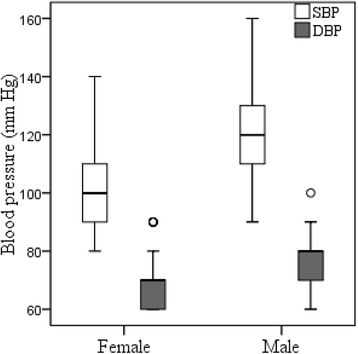
Method: The data was collected on 184 adult university students (118 female and 66 male) in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Anthropometric, BMR details and an average of at least two blood pressure measurements were obtained. Hypertension was defined by a systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥ 140 mmHg and/or, diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥ 90 mmHg.
Results: Overall, 6.5% of participants had hypertension with significantly (p < 0.001) higher prevalence in male (12.1%) than in the female (3.4%) students. Age and BMI showed positive and significant correlation with hypertension among the students. When adjusted for body mass index (BMI), as well as other potentially confounding variables such as age, sex, smoking status and degree of urbanization, BMR was positively correlated with SBP and DBP (p < 0.001). Thus, higher BMR is associated with SBP and DBP; this is opposite the well documented inverse relationship between physical activity and blood pressure. If the influence of BMR on blood pressure is confirmed, the systematically elevated BMR might be an important predictor that can explain relatively high blood pressure and hypertension in humans.
Conclusion: This study reports the prevalence and associated risk factors of hypertension in the Bangladeshi adult students. The study also showed a positive association between BMR and blood pressure among the participants. A large scale longitudinal study across the country is needed to find out the underlying causes of hypertension in the Bangladeshi adults. In addition, comprehensive and integrated intervention programs focusing on modifiable risk factors are recommended to make awareness and prevent hypertension.
Keywords: Bangladesh; Basal metabolic rate; Body mass index; Hypertension.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Gonoshasthaya Samaj Vittik Medical College, Savar, Dhaka-1344, Bangladesh. All participants were informed about the study and they gave their written consent before inclusion in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors have no competing of interests to declare.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Alwan A, (2010) World Health Organization Global status report on noncommunicable diseases. Available at: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44579/1/9789240686458_eng.pdf
-
- Barker DJP, Godfrey KM. Maternal nutrition, fetal programming and adult chronic disease. In: Gibney MJ, Margetts BM, Kearney JM, Arab L, editors. Public health nutrition. Oxford: Blackwell; 2004. pp. 302–316.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical