Androgenic-anabolic steroids inhibited post-exercise hypotension: a case control study
- PMID: 28743567
- PMCID: PMC5816078
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjpt.2017.07.001
Androgenic-anabolic steroids inhibited post-exercise hypotension: a case control study
Abstract
Background: There is evidence of hypertensive effects caused by anabolic androgenic steroids (AAS). A single exercise session promotes the acute reduction of blood pressure, but the effects of AAS on this phenomenon are unknown.
Objectives: To investigate the post-exercise blood pressure response in androgenic-anabolic steroid users.
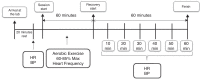
Methods: Thirteen AAS users (23.9±4.3 years old) and sixteen controls (22.1±4.5 years old) performed a session of aerobic exercise. Heart rate and blood pressure were assessed before exercise and during a 60min post-exercise resting period. Repeated ANOVA measures were used to determine differences between the groups.
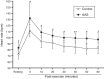
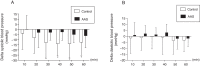
Results: While the control group had a significant reduction in post-exercise systolic blood pressure of up to 13.9±11.6mmHg at 40min, this phenomenon was limited among AAS users who reached a maximum of 6.2±11.5mmHg at 60min. The between groups comparison revealed significant higher post-exercise hypotension (PEH) for the control group at 30min (-12.9±14.1mmHg versus -2.9±7.6mmHg), 40min (-13.9±11.6mmHg versus -2.5±8.3mmHg), 50min (-13.9±13.9mmHg versus -5.0±7.9mmHg) and 60min (-12.5±12.8mmHg versus -6.2±11.5mmHg). There was no significant diastolic PEH in any of the groups.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated impaired systolic post-exercise hypotension as a new adverse effect of AAS usage.
Keywords: Anabolic agents; Blood pressure; Exercise; Movement; Physiological adaptation.
Copyright © 2017 Associação Brasileira de Pesquisa e Pós-Graduação em Fisioterapia. Publicado por Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Sagoe D., Molde H., Andreassen C.S., Torsheim T., Pallesen S. The global epidemiology of anabolic-androgenic steroid use: a meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis. Ann Epidemiol. 2014;24(5):383–398. - PubMed
-
- Marocolo M., Maior A.S., Katayama P.L. Anabolic steroid treatment induces cardiac autonomic dysfunction in rats: time-course of heart rate variability. Am J Biomed Eng. 2013;3(3):54–62.
-
- Santos M.A.P., Oliveira C.V.C., Silva A.S. Adverse cardiovascular effects from the use of anabolic-androgenic steroids as ergogenic resources. Subst Use Misuse. 2014;49(9):1132–1137. - PubMed
-
- Cunha T.S., Tanno A.P., Costa Sampaio Moura M.J., Marcondes F.K. Influence of high-intensity exercise training and anabolic androgenic steroid treatment on rat tissue glycogen content. Life Sci. 2005;77(9):1030–1043. - PubMed
-
- Marcon E.R., Gus I., Neumann C.R. Impact of a minimum program of supervised exercises in the cardiometabolic risk in patients with morbid obesity. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2011;55(5):331–338. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

